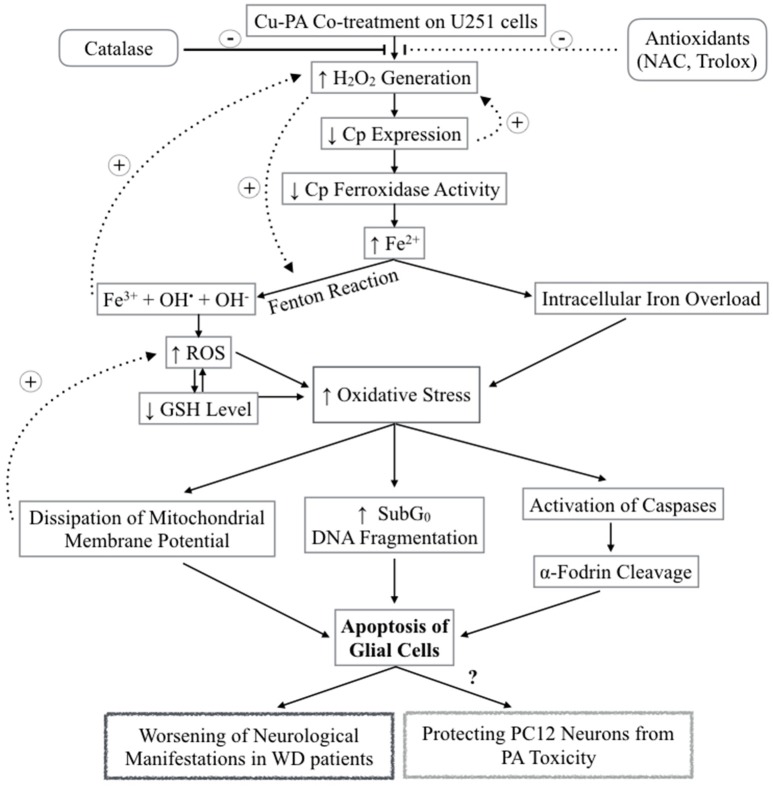
Figure 12.
Schematic Diagram summarizing the effect of Cu-PA treatment on neural cells H2O2 generation increases following Cu-PA treatment on U251 Glial cells. Entry of H2O2 into the cells increases oxidative stress intracellularly. Alternatively, it mobilizes intracellular copper leading to a decrease in CP expression. Decrease in level of incorporated Cp copper would decrease ferroxidase activity involved in iron loading onto iron binding/transporting proteins. The increase in Fe3+ in presence of H2O2 generates hydroxyl radicals and increases ROS level leading to a decrease in GSH level. Consequences of the increased oxidative stress are: dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential that triggers apoptotic events; increase in SubG0 phase /DNA fragmentation; and activation of caspases causing proteolytic cleavage of α-fodrin eventually leading to cell death of U251 glial cells. Catalase enzyme protected completely treated U251 cells whereas NAC and Trolox were partially protective.