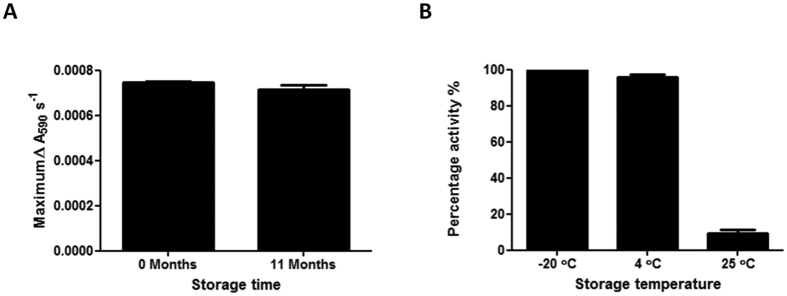
Figure 7.
(A) Holo-BpsA was assayed for activity (maximal reaction velocity) before and after storage at −20 °C for 11 months. In each case a master mix containing 2 μM holo-BpsA, 50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8.5, 20 mM MgCl2, 5 mM ATP and ddH2O to a final volume of 90 μL was dispensed into individual wells of a 96 well plate. The reaction was initiated by the addition of 10 μL 1000 μM L-glutamine in ddH2O. The 96 well plate was shaken at 1000 rev/min for 10 s and the A590 values were recorded every 10 s for 1 h. The maximal velocity of the reaction was calculated by finding the maximum slope value as previously described26. Data are the means of three replicates and error bars indicate standard error of the mean. (B) BpsA was assayed for activity (maximal reaction velocity) before and after storage at either −20 °C, 4 °C or 25 °C for 24 weeks. To convert the apo-BpsA to holo-BpsA prior to activity assays the following reaction mix was used: 2 μM BpsA, 12.5 μM Co-enzyme A, 0.1 μM Sfp, 5 mM MgCl2, 50 mM Tris pH 7.8 and ddH2O to a total volume of 25 μL per reaction. Reactions were incubated at 30 °C with shaking at 200 rev/min for 30 min to ensure complete conversion to holo-BpsA. Next, 25 μL of the holo-BpsA mix was dispensed into individual wells of a 96 well plate, each containing 50 μL of 50 mM Tris-Cl pH 7.8 and 5 mM MgCl2 in ddH2O. Indigoidine synthesis was initiated by the addition of 25 μL of 5 mM ATP and 2 mM L-glutamine in ddH2O (concentrations are per final 100 μL reaction volume). The 96 well plate was then incubated at 25 °C with shaking at 1000 rev/min for 10 s and the A590 values were recorded every 20 s for 1 h. The velocity of the reaction was calculated by finding the maximum slope value as above, and percentage activity was calculated for each sample relative to the pre-storage level of activity. The graph bars are the mean of three replicates and the error bars indicate the standard error of the mean.