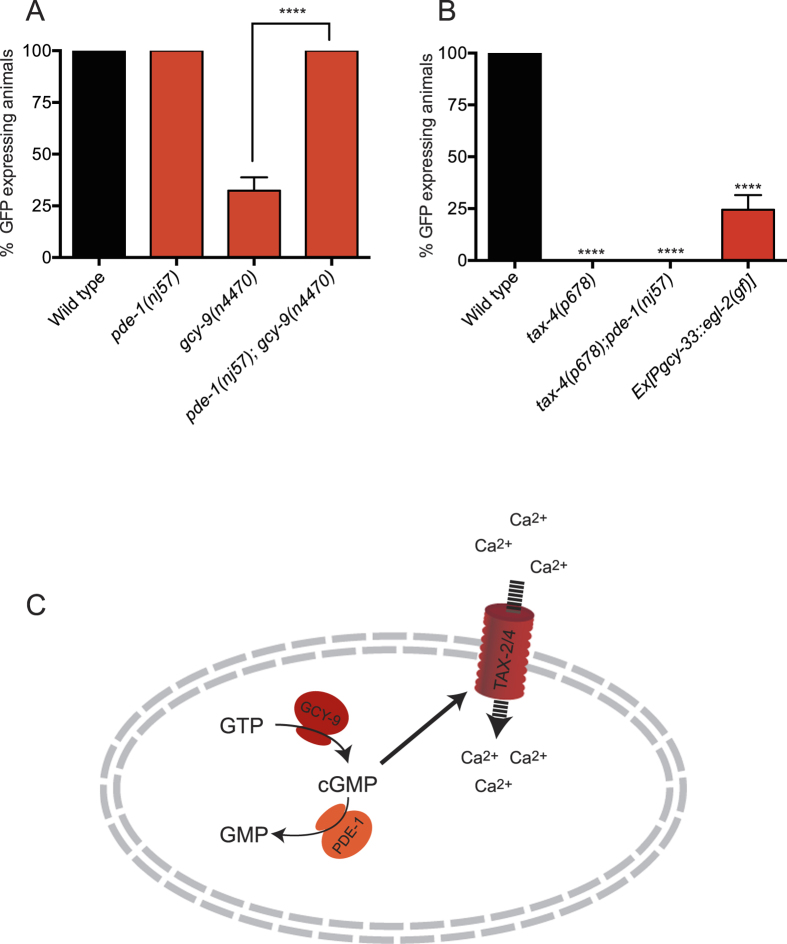
Figure 3. cGMP Levels Regulate flp-19::GFP Expression in the BAG Neurons.
(A) Quantification of the flp-19::GFP reporter suggests that the guanylate cyclase GCY-9 and the phosphodiesterase PDE-1 exhibit opposing regulation of cGMP levels in the BAG neurons. The pde-1(nj57) mutant exhibits wild type expression of flp-19::GFP in the BAG neurons while gcy-9(n4470) mutants exhibit a strong defect in expression. In gcy-9(n4470); pde-1(nj57) double mutant animals, flp-19::GFP expression in the BAG neurons is restored, suggesting that cGMP levels in the BAG neurons regulate flp-19::GFP expression. See Materials and Methods for neuronal scoring criteria used. n > 50. ****P < 0.0001. (B) flp-19::GFP in the BAG neurons is completely abrogated in tax-4(p678) mutant animals. Furthermore, the tax-4(p678) mutant defect in flp-19::GFP expression cannot be rescued by mutation in pde-1 indicating that tax-4 acts downstream of cGMP signaling. Expression of an constitutively active form of EGL-2 in the BAGs also reduces flp-19::GFP expression indicating that flp-19::GFP expression is activity dependent. See Materials and Methods for neuronal scoring criteria used. n > 50. ****P < 0.0001. (C) Schematic model of cGMP regulation in the BAG neurons. GCY-9 converts GTP into cGMP, while PDE-1 catalyzes the conversion of cGMP into GMP. cGMP opens the TAX-2/TAX-4 channels leading to an influx of calcium and activation of the neuron.