Figure 8.
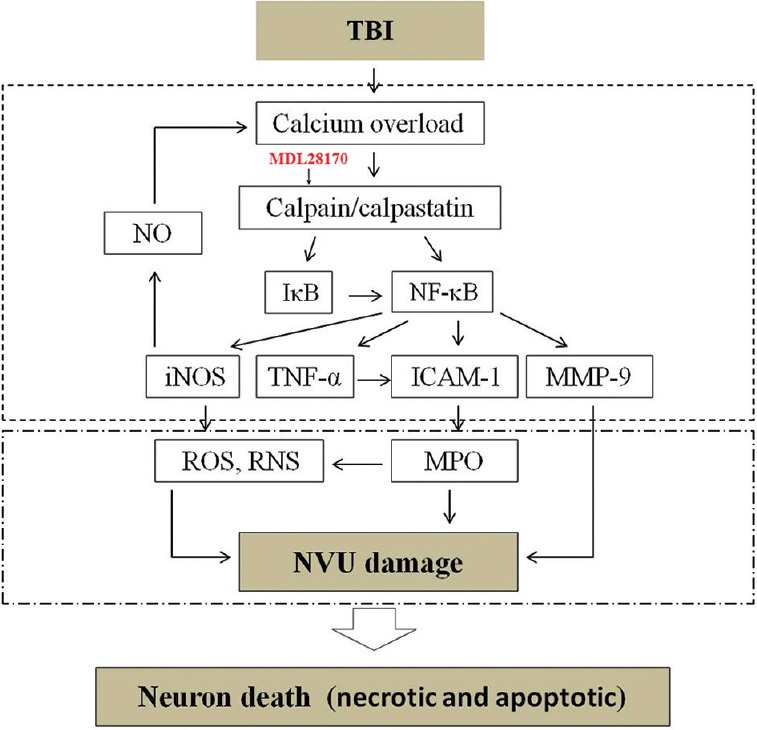
Schematic diagram showing the relationship of calpain/NF-κB/inflammation/NVU damage after CCI in mice. Traumatic brain injury induces calcium overload, which, in turn, upregulates calpain. Calpain may downregulate IκB and activate NF-κB. NF-κB induces activation of TNF-α, iNOS, ICAM-1, and MMP-9. These inflammatory substances induce degradation of basal lamina and tight junction proteins, resulting in NVU disruption, leading to brain edema. MDL28170 could reverse those changes. NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; NVU: Neurovascular unit; CCI: Controlled cortical impact; IκB: Inhibitory-κB; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; ICAM-1: Intracellular adhesion molecule-1; MMP-9: Matrix metalloproteinase-9.
