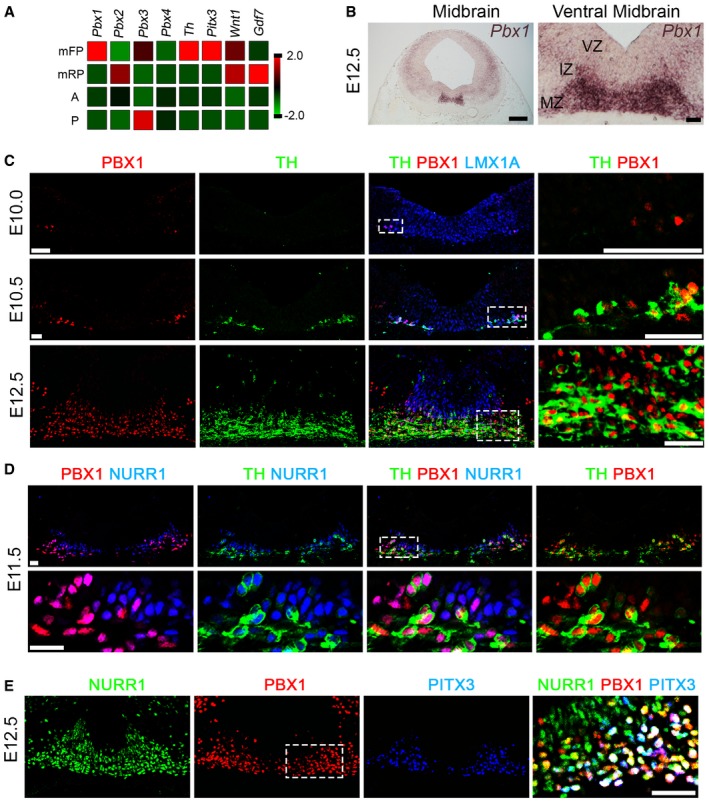
Tru‐Seq RNA sequence analysis of E12.5 midbrain floor plate (mFP), midbrain roof‐plate (mRP), anterior (A, adjacent anterior FP), and posterior (P, adjacent posterior FP). Pbx1 is enriched in the midbrain FP, together with Th and Pitx3. Lower levels of Pbx3 are also expressed in the mFP. Gdf7 and Wnt1 are restricted to the mRP at E12.5.
Pbx1 is expressed in the intermediate (IZ) and marginal zones (MZ), but not the ventricular zone (VZ), of the mFP at E12.5, as detected by in situ hybridization.
PBX1 is first detected in the ventro‐lateral part of the LMX1A+ domain at E10, preceding the birth of the first (TH+) mDA neurons at E10.5. At E12.5, PBX1 is present in all mDA neurons, but not all PBX1+ cells are TH+. White boxes indicate the area shown in higher magnification (right).
At E11.5, PBX1 protein defines a subpopulation of NURR1+ neuroblasts and labels all NURR1+TH+ mDA neurons.
PBX1 co‐localizes with PITX3 and is also detected in a subpopulation of NURR1+PITX3− postmitotic neuroblasts at E12.5. Higher magnification revealed three different populations of postmitotic cells: primary neuroblasts (NURR1+PBX1A−PITX3− cells, green), secondary neuroblasts (NURR1+PBX1A+PITX3− cells, yellow/orange), and tertiary neuroblasts/mDA neurons (NURR1+PBX1A+PITX3+ cells, white).
Data information: Nuclear staining, Dapi (4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole, blue). All scale bars, 20 μm.