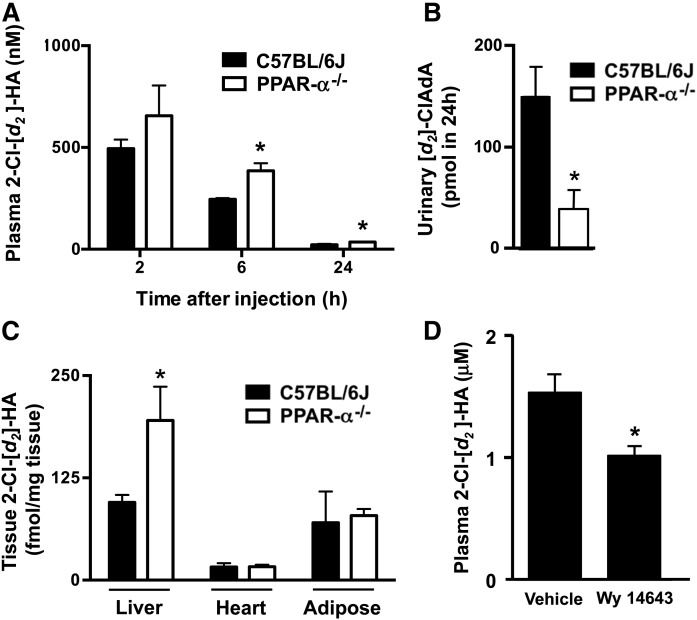
Fig. 4.
Plasma 2-ClHA clearance is reduced in PPAR-α−/− mice. Male PPAR-α−/− mice (open bars) and wild-type C57BL/6J mice (closed bars) were treated with 2-Cl−[d2-4,4]HA (0.35 mg/100 g body weight) with plasma collected at indicated times (A) and urine collected over 24 h (B) post intraperitoneal treatment with subsequent analysis of 2-Cl−[d2-4,4]HA (A) and [d2]ClAdA (B), as described in the Materials and Methods. Similarly, tissue levels of 2-Cl−[d2-4,4]HA were analyzed (C). Values are the mean ± SEM with n = 5 per group. *P < 0.05 for comparisons between PPAR-α−/− mice and wild-type C57BL/6J mice. Male wild-type C57BL/6J mice were treated with vehicle or Wy 14643 (10 mg/kg/day ip) for 2 days before 2-Cl−[d2-4,4]HA (0.9 mg/100 g body weight) was administered (D). Three hours later, blood was collected and plasma 2-Cl−[d2-4,4]HA was analyzed as described in the Materials and Methods. *P < 0.05 for comparison between Wy 14643 treatment and vehicle.