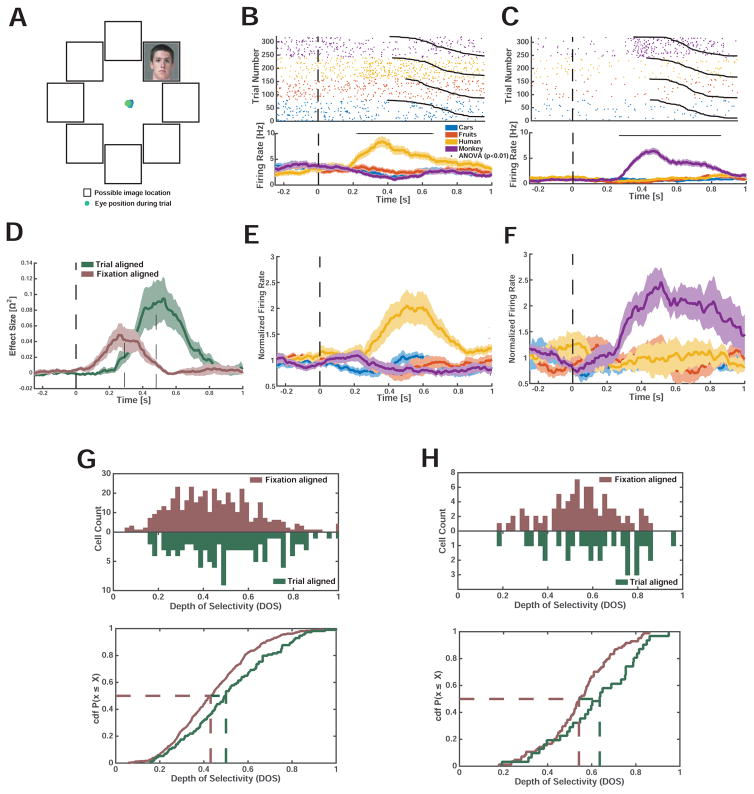
Figure 7. Face-selective amygdala neurons recorded in humans respond to covertly attended faces.
(A) Subjects fixated at the center of the screen and indicated by button press whether a peripheral image depicted a car. Shown is a single example trial, with eye tracking data (blue) indicating that subjects maintained fixation. (B–C) Example face selective neurons with a response selective to the identity of the peripheral stimulus. t=0 is stimulus onset. (D) Comparison of response of face cells in covert and free-viewing sessions for the subset of cells which were recorded in both tasks (4/7 sessions, n=10). The average effect size is shown fixation-and trial onset aligned. (E) PSTH of all human face-selective neurons (Hh, n=16) during the fixation-enforced covert attention condition. (F) PSTH of all monkey face-selective neurons (Hm, n=9) during the fixation-enforced covert attention condition. (G,H) Population-level comparison between the covert and free-viewing tasks for all recorded (G) and only visually tuned (H) cells. (G) DOS values were significantly larger in the covert attention task compared to the free viewing task (p<0.01, 2-sample KS test). (H) DOS values were selectivity higher in the covert attention task (p<0.05, 2-sample KS test).