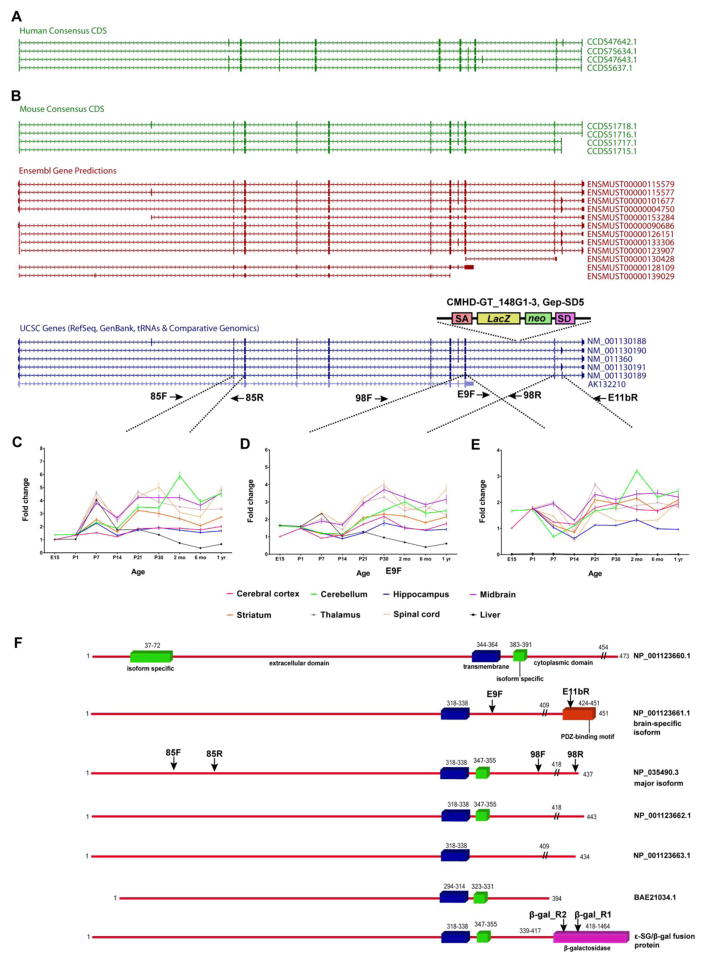
Fig. 1.
(A) Human SGCE Consensus CDS isoforms. (B) Mouse Sgce isoforms derived from Consensus CDS, Ensembl gene predictions and UCSC genes showing the location of the CMHD-GT_14G1-3 Gep-SD5 gene trap. Three distinct primer pairs (C, 85F/85R; D, 98F/98R; and E, E9F/E11bR) were designed to examine Sgce expression in eight different tissues across nine developmental time points. (F) Protein structures of the major (NP_035490.3), longest (NP_001123660.1), brain-specific (NP_001123661), and shortest (BAE21034.1) mouse isoforms, and predicted chimeric ε-SG/β-gal fusion protein derived from the major isoform. Blue bars, transmembrane domain. Green bars, isoform specific domains. Red bar, protein sequence derived from exon 11b that includes a PDZ-binding motif. Pink bar, β-galactosidase.//, predicted sites of ε-SG/β-gal protein fusion. Also shown are the approximate locations of primers that would amplify the corresponding regions of Sgce and hybrid transcripts. SA, splice acceptor. lacZ, gene encoding β-galactosidase. neo, neomycin resistance gene. SD, splice donor.