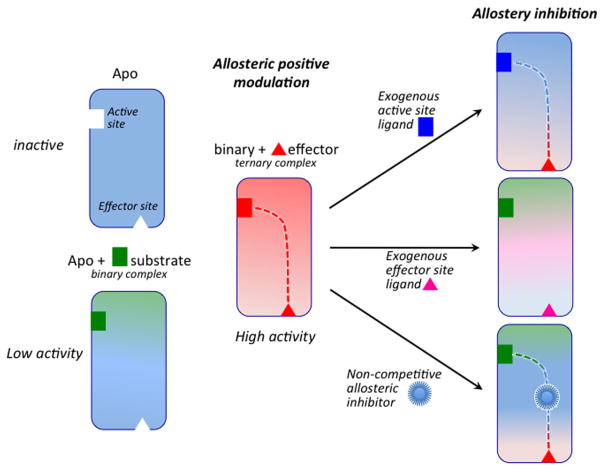
Figure 1.
Basal (low or negligible) catalytic activity of the apoenzyme observed in the presence of substrate (green) but no endogenous effector (red). Positive allosteric modulation by effector binding >10 Å from the active site increases enzymatic activity. The two sites communicate through an allosteric pathway (red dotted line). Enzymatic activity is inhibited upon binding of competitive exogenous ligands at the active or effector sites. Noncompetitive ligands disrupt allosteric communication upon binding at critical sites along the allosteric pathway.