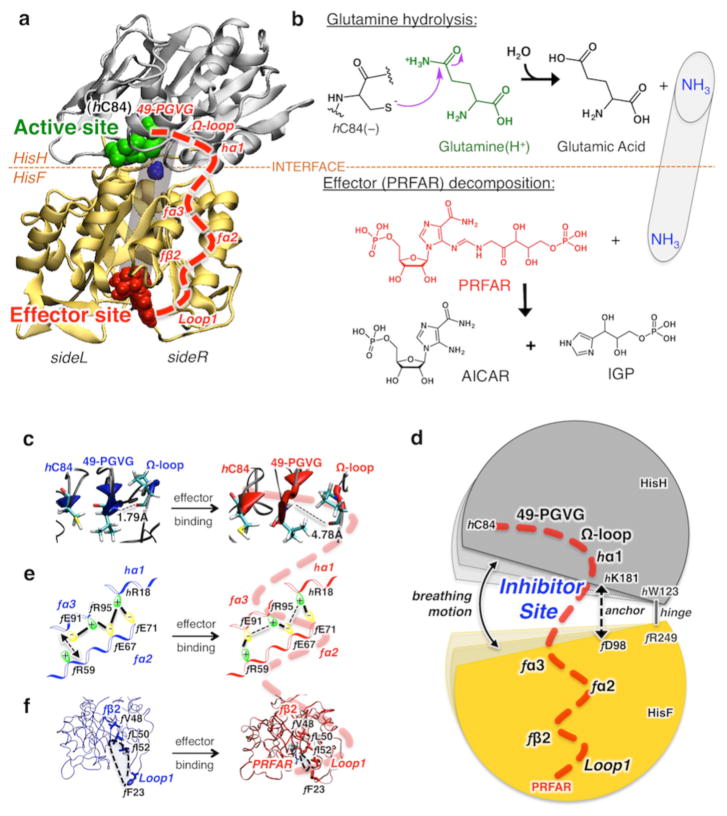
Figure 2.
Glutamine hydrolysis, catalyzed by IGPS at the HisH active site, initiated after binding of the effector (PRFAR) to HisF and allosteric communication. (a) Tertiary structures of the HisH and HisF domains of IGPS, showing the active site (green), the allosteric site (red), and a schematic representation of the internal ammonia (blue) channel (gray tube). The allosteric pathway (red dashed line) involves secondary structures (labeled in red) on the right side (side R) of the complex. (b) Schematic representations of glutamine hydrolysis and effector decomposition at the active and effector sites. (c–f) The allosteric communication involves structural changes induced by binding of PRFAR (red) to the apo complex (blue), affecting the IGPS breathing motion targeted by small molecule inhibitors that bind at the HisF–HisH interface.