Figure 2. The TRC40 pathway mediates the insertion of otoferlin into mammalian ER‐derived microsomes.
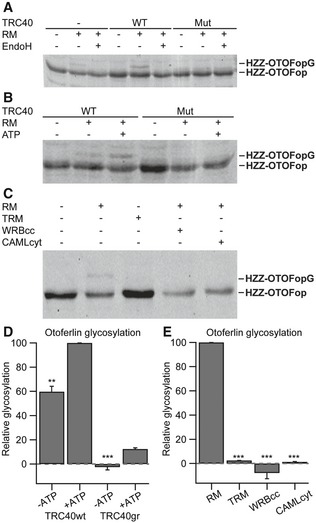
- HZZ‐OTOFop, carrying a C‐terminal glycosylation site (opsin tag), was purified alone or in complex with wild‐type or an ATPase‐deficient mutant version of TRC40 and incubated in the absence or presence of ER‐derived rough microsomes (RM). Membrane integration (glycosylation) was monitored by SDS–PAGE and immunoblot using an anti‐opsin antibody. Where indicated, EndoH was used to remove N‐linked oligosaccharides.
- HZZ‐OTOFop in complex with wild‐type or mutant TRC40 was incubated with RM in the presence or absence of ATP and membrane insertion was monitored by opsin‐specific immunoblot.
- HZZ‐OTOFop in complex with wild‐type TRC40 was incubated in the presence of RM or trypsin‐treated rough microsomes (TRM), and in the presence of WRBcc or CAMLcyt. Membrane insertion was monitored by opsin‐specific immunoblot.
- Quantification of relative protein glycosylation shown in (B) (n = 3). Data are represented as means ± SEM. TRC40gr, mutated version of TRC40; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (Student's two‐sample t‐test).
- Quantification of relative protein glycosylation of the data shown in (C) (n = 3). Data are represented as means ± SEM. ***P < 0.001 (Student's two‐sample t‐test).
Source data are available online for this figure.
