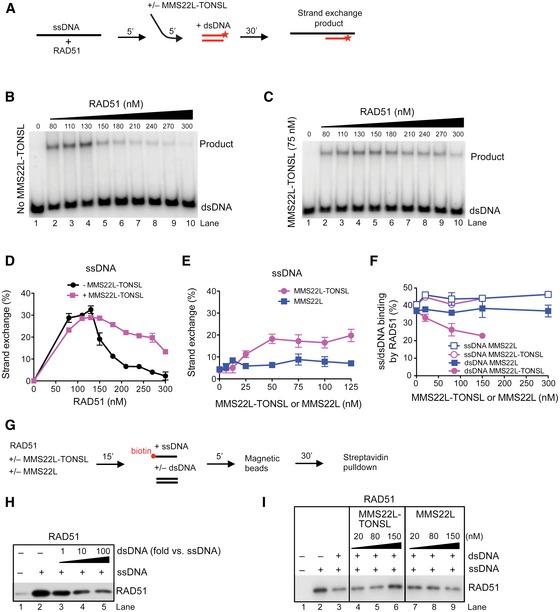
-
A
Schematic representation of the DNA strand exchange assay with ssDNA.
-
B, C
Strand exchange assay with ssDNA and RAD51, and with (C) or without (B) the addition of MMS22L–TONSL (75 nM).
-
D
Quantification of (B, C) shows averages, n = 2; error bars, SEM.
-
E
Averages of quantified strand exchange assays with ssDNA, RAD51 (270 nM), and varying concentrations of MMS22L–TONSL or MMS22L. n = 2; error bars, SEM.
-
F
Quantification of electrophoretic mobility shift assays with dsDNA or ssDNA, RAD51, and MMS22L–TONSL or MMS22L. Averages shown, n = 2; error bars, SEM.
-
G
A scheme of streptavidin pulldown assay performed in (H, I).
-
H
A representative immunoblot showing the effect of increasing amounts of dsDNA on RAD51 binding to ssDNA (1 nM).
-
I
A representative immunoblot showing effects of MMS22L–TONSL and MMS22L titration into reactions containing RAD51, ssDNA (1 nM), and dsDNA (10 nM), as indicated.