Figure 1.
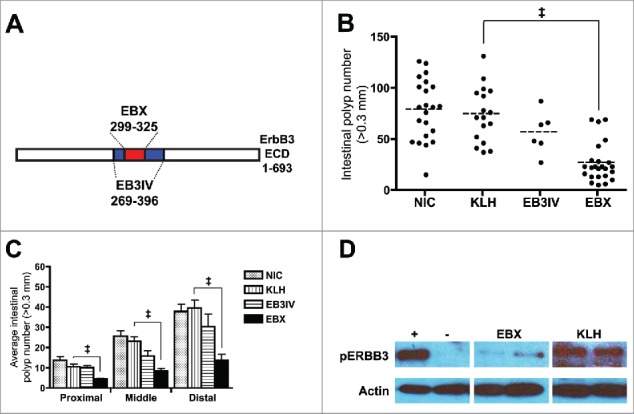
EBX peptide inhibits polyp formation. (A) Schematic showing relation of EBX peptide (ERBB3 residues 299–325) and EB3IV recombinant protein (ERBB3 residues 269–396) to ERBB3 extracellular domain (ECD). (B) Polyp burden in 100 day old ApcMin mice after no treatment (NIC) or treatment with carrier protein (KLH), recombinant protein (EB3IV) or peptide (EBX). Mice were treated at 3, 5, and 9 weeks following birth. The dashed line represents the mean for each group. (C) Mean polyp burden for different portions of the intestinal tract from ApcMin mice treated with KLH, EB3IV, EBX, or control. (D) Erbb3 activation assay in SW620 cells with (+) or without (−) 12.5 nM neuregulin in the presence of sera from two separate EBX-or KLH-immunized mice. All error bars show means ± SEM Statistics: ‡p < 0.001; **p < 0.01.
