Figure 3.
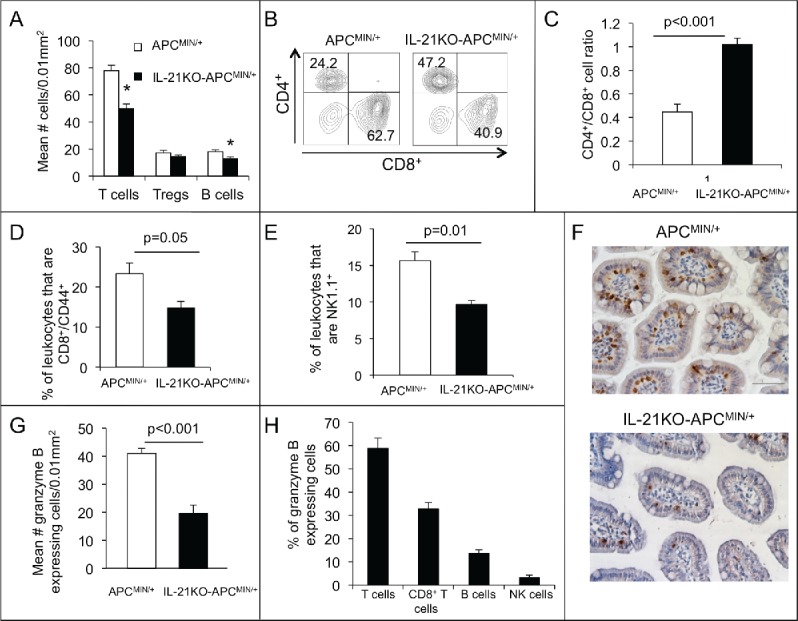
Deficiency of IL-21 in APCMIN/+ mice results in decreased infiltrating T cells, effector memory T cells, B cells, NK cells, and granzyme B-expressing cells with an increased CD4+/CD8+ ratio. (A) Density of CD3+ (T cells), FoxP3+ (Tregs), and B220+ cells (B cells) in sections of paraffin-embedded ileum as determined by immunohistochemistry (n = 6 per group).*p < 0.05. Flow cytometry was performed on leukocytes isolated from ileum and gated on live, single, CD45+ cells. Representative density plots of CD4+ and CD8+ cells among CD3+ cells (B) and a histogram of the of CD4+/CD8+ cell ratio (C) are shown (n = 4 per group). The percentage of CD8+CD44+ (D) or NK1.1+ (E) leukocytes is compared (n = 4 per group). (F) Granzyme b-expressing cells were determined by immunohistochemical staining of ileum. (G) The density of granzyme b-expressing cells is shown (n = 6 per group). (H) The percentage of granzyme b-expressing cells that also express CD3 (T cells), CD8 (CD8+ T cells), B220 (B cells), and NKp46 (NK cells) was determined in APCMIN/+ mouse intestine by immunofluorescent staining of ileum (n = 3). All mice were 15-week old.
