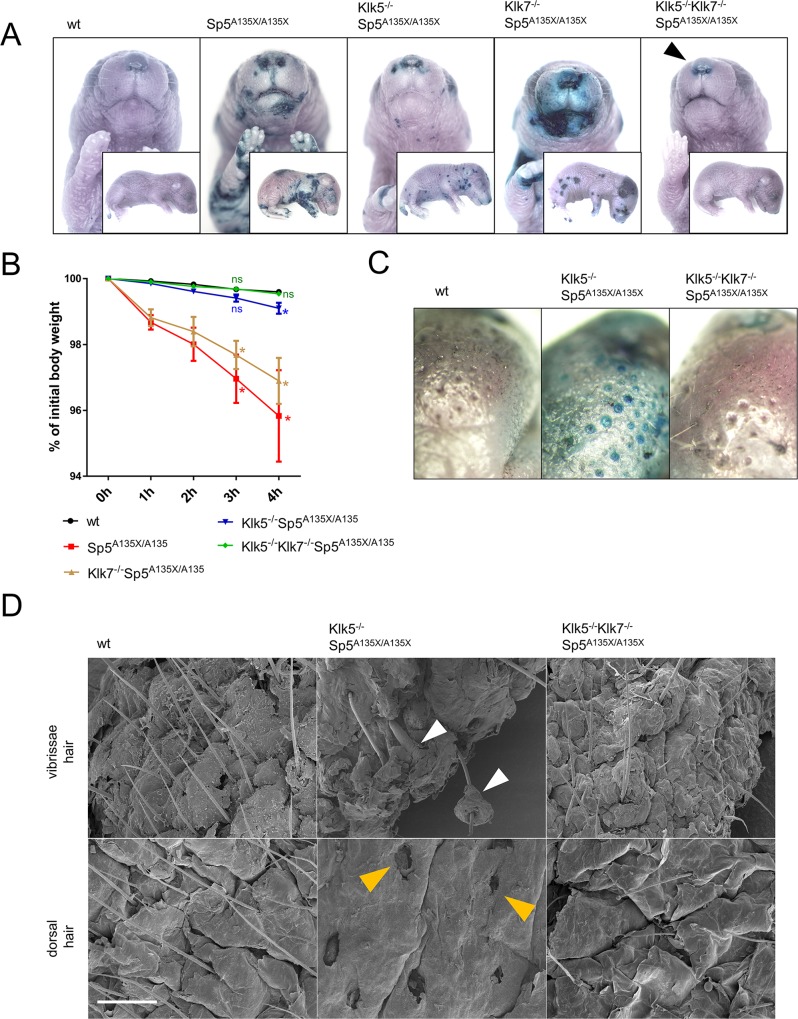
Fig 4. Analysis of skin-barrier abnormalities.
(A) Newborn (P0) pups were analysed by barrier penetration assay using toluidine blue (TB). Remaining barrier-defect in the area of nostrils of Klk5-/-Klk7-/-Sp5A135X/A135X pups in the vicinity of nostrils is marked by black arrowhead (B) TEWL analysis of P0 pups as a reduction of body-weight over time, n≥4 for each genotype. Error bars represent standard errors of mean; Klk/Spink5 mutant lines were compared with the wt line using Mann-Whitney U-test at 3h and 4h, ns means “not significant“; * p < 0.05 (C) Epidermal barrier in P5 Klk5-/-Sp5A135X/A135X pups was compromised in the proximity of hair follicles (D) Vibrissae hair (upper panel) and dorsal skin (lower panel) obtained from P5 pups analysed using scanning electron microscopy. Defective separation of hair shafts from the root sheath in Klk5-/-Sp5A135X/A135X is marked by white arrowhead. Dorsal skin of Klk5-/-Sp5A135X/A135X mice showed complete absence of hair shafts and exposed upper parts of hair follicles (yellow arrowheads); Scale bar, 300 μm.