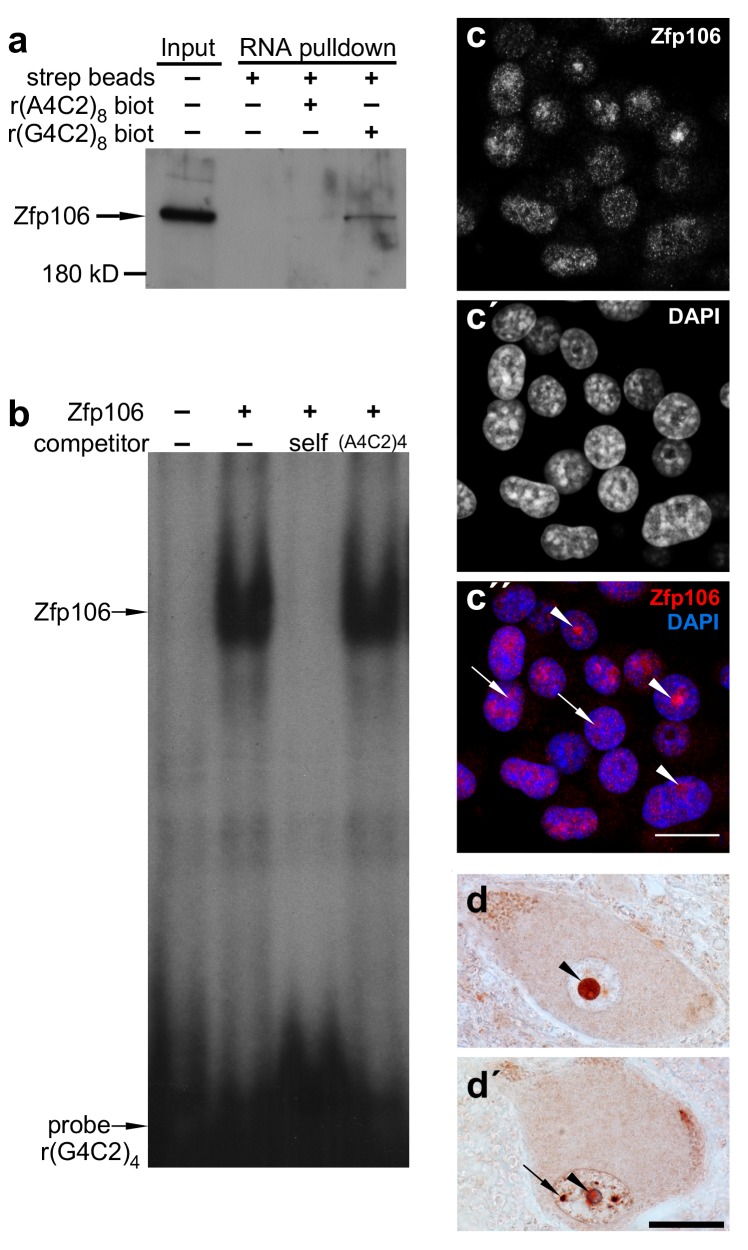
Figure 1. Zfp106 is an rGGGGCC binding protein.
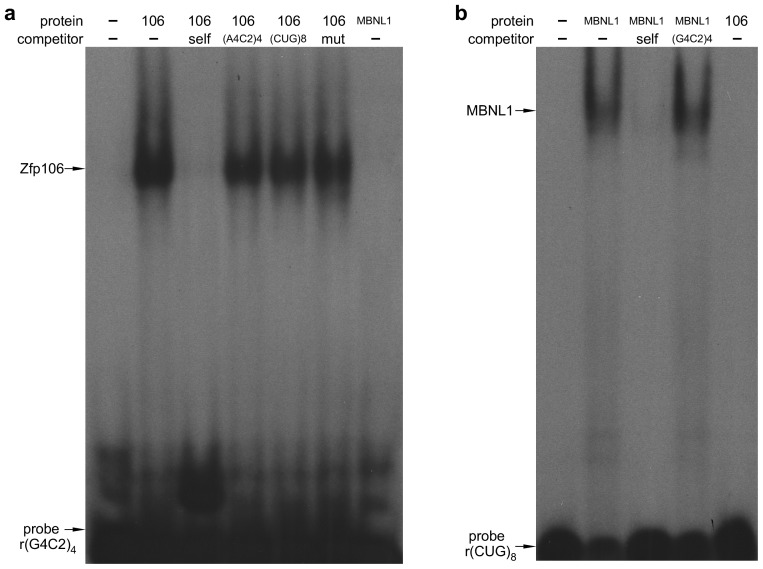
(a) Western blot analysis of Zfp106 eluted from a biotinylated-RNA pulldown of Neuro-2a nuclear proteins. Endogenous Zfp106 was specifically pulled down by (GGGGCC)8 biotinylated RNA and not by the unrelated (AAAACC)8 biotinylated RNA oligonucleotide. (b) RNA EMSA performed with purified Zfp106 protein demonstrates that Zfp106 directly binds (GGGGCC)4 RNA in vitro. 30× molar excess of unlabeled self competitor, but not 30× r(AAAACC)4, competes with Zfp106 binding to r(GGGGCC)4, establishing specificity of the interaction. (c) Immunofluorescence with an anti-Zfp106 antibody detects Zfp106 expression in the nucleolus (arrowheads) and in other discrete nuclear puncta (arrows) in cultured Neuro-2a cells. The three images are the same section showing the red channel in (c), the blue channel in (c′), and both channels in (c′′). Scale bar, 20 μm. (d, d′) Immunohistochemical detection of human ZNF106 shows strong nucleolar expression in human motor neurons in the anterior horn of spinal cord. The two images are from different post-mortem individuals. Arrowheads mark nucleolar ZNF106 expression; arrows mark other nuclear and perinucleolar foci of ZNF106 expression. Scale bar, 25 µm.