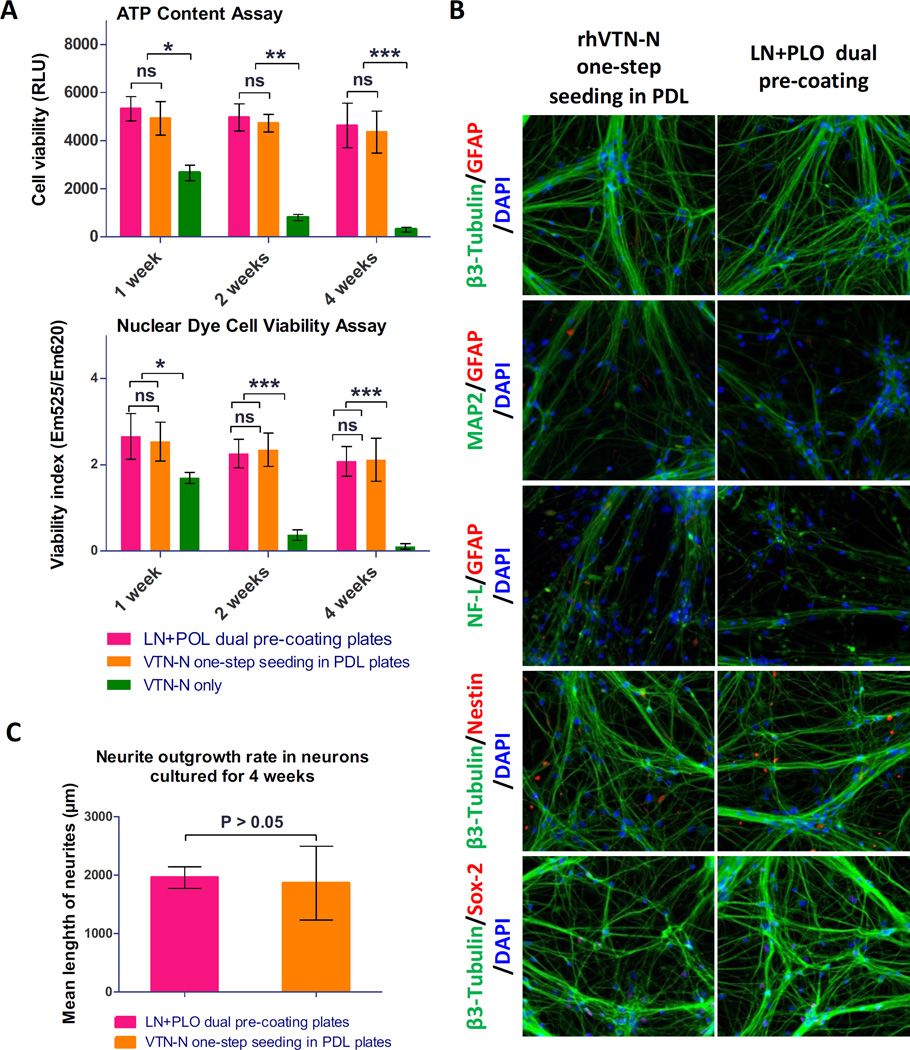
Figure 2.
Results of direct seeding of NSCs for neuron differentiation. (A): Results of cell viability determined in the ATP content and nuclear dye assay in neurons differentiated from NSCs. Cells directly seeded in commercial 384-well PDL-coated plates with the rhVTN-N-supplemented medium showed similar cell viability as those control cells plated in the traditional LN + PLO dual-coated plates (p > 0.05). However, neurons differentiated from NSCs directly seeded in regular (non-coated) 384-well plates with the rhVTN-N-supplemented medium exhibited low cell viability (***p<0.05). Data are represented as the mean ± SEM of at least triplicates. (B): Images of neurons differentiated from the direct seeding of NSCs in rhVTN-N-supplemented medium compared to the control condition of LN + POL plate pre-coating neurons. The NSCs differentiated to neurons with similar positive staining of β-III Tubulin, MAP2, and NF-L neuronal markers as the control cells cultured in LN + PLO dual-coated plates. The neurons also exhibited positive SOX-2 staining; they were negative for the markers Nestin, and GFAP (an astrocyte marker). (C): rhVTN-N The β-III Tubulin stained neurites were measured after 4 weeks of differentiation in assay plates. The neurite outgrowth rate of neurons differentiated from NSCs directly seeded in commercial 384-well PDL-plates with rhVTN-N-supplemented medium was similar to that of NSCs seeded in LN + PLO dual-coated plates (p>0.05). Data are represented as the mean ± SEM of at least triplicates.