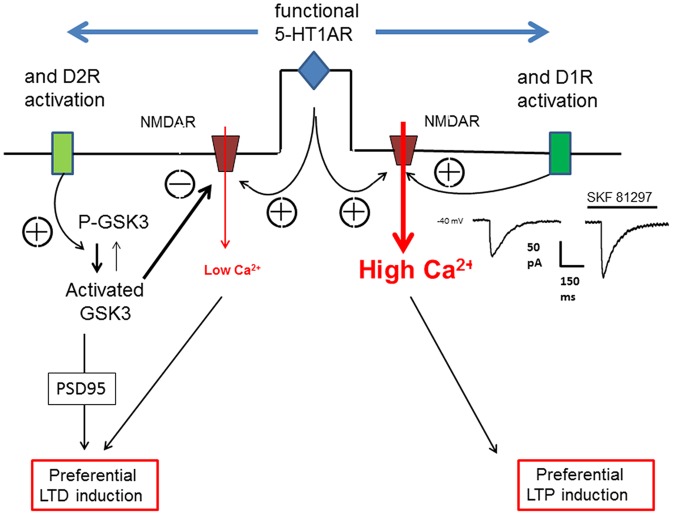
Figure 3.
Schematic view of the action of 5-HT1AR on D1R or D2R to orientate the plasticity of an excitatory synapse in the PFC. The orientation of synaptic plasticity by dopamine (DA) acting at either D1Rs or D2Rs is dependent on the concomitant activation of 5-HT1ARs. We assume that the induction of either LTP or LTD of excitatory synapses depends on the magnitude of calcium transient (controlling AMPARs trafficking) within the dendritic spines which is determined by the calcium influx through NMDARs. Therefore, an increased calcium transient (High Ca2+) following 5-HT1AR and D1R activation (see the NMDA current on the right inset) would lead to LTP whereas a reduced calcium transient (low Ca2+) following 5-HT1AR and D2R activation would lead, via the activation of glycogen-synthase kinase-3 (GSK3), to LTD.