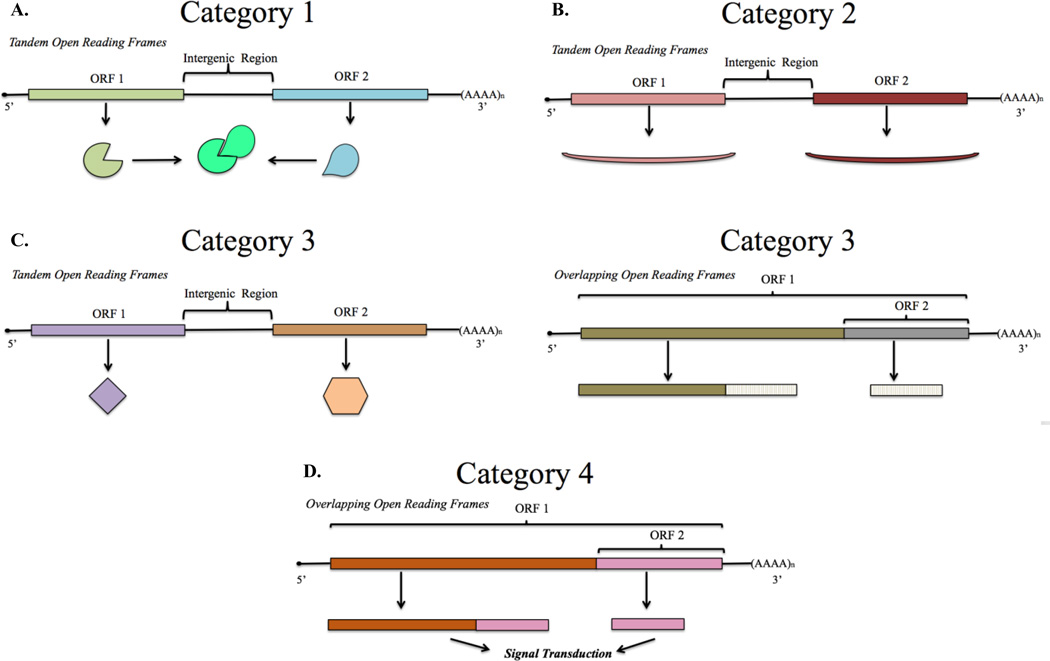
Figure 1. Functional Organization of Bicistronic Genes.
A. Two subunits of a multi-subunit complex whose expression is coordinated in a single transcript: each Open Reading Frame (ORF) codes for a specific subunit of a larger protein complex. B. Functionally similar gene products that are differentially co-expressed: a primary protein is expressed through canonical cap-dependent translation while a secondary and functionally similar protein is differentially expressed through a cap-independent mechanism. C. Functionally distinct gene products that have programmatically-related expression: expression of two differentially functioning proteins is coupled with their operation in a particular biological pathway. Category 3 appears with both tandem and overlapping reading frames. D. Signaling proteins generated by stimulus-coupled protease cleavage or by cap-independent translation: two overlapping ORFs code for necessary products for signal transduction, the primary product is a receptor that initiates signal transduction upon ligand binding while the secondary product is a constitutively active signal.