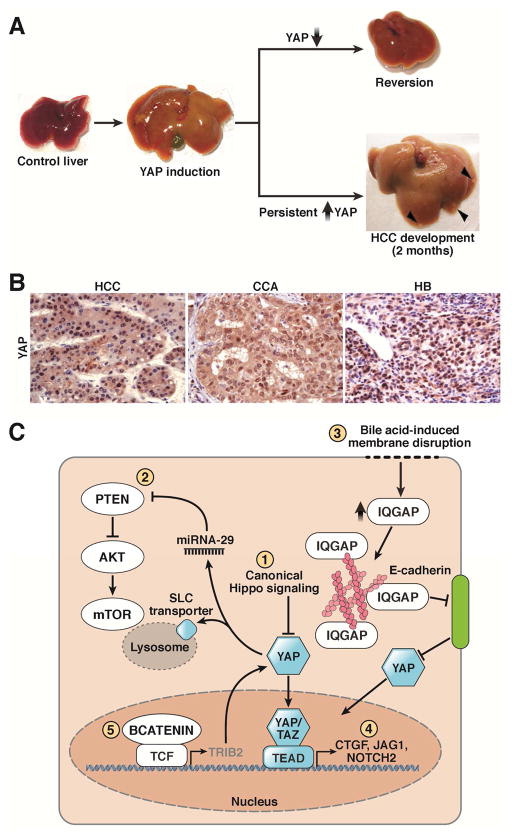
Figure 3. Effects of Yap Overexpression in the Liver.
A. Liver-specific overexpression of YAP leads to massive hepatomegaly with livers approaching 4–5x their original size. Upon restoration of endogenous levels of YAP, the liver returns to its usual size19. Persistent YAP activation for 2 months frequently results in HCC development (Arrowheads).
B. Increased overall YAP and nuclear YAP is a feature of several liver cancers, including HCC, CCA, and HB115.
C. YAP can mediate its tumorigenic effects either autonomously or through synergy with other pathways. YAP can be activated through canonical Hippo inactivation (1) or non-canonical membrane-associated signaling (2). YAP can also interact with the PI3K–Akt–mTOR pathway through a microRNA-mediated mechanism or via upregulation of lysosomal SLC transporters (3). Finally, YAP can interact with the NOTCH and Wnt pathways, as evidenced through upregulation of NOTCH ligands and receptors (4) and YAP’s stabilization by the Wnt target gene TRIB2 (5).