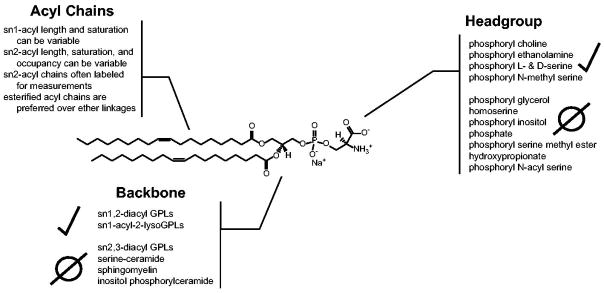
Figure 3. The anatomy of a P4-ATPase phospholipid substrate.
A dioleoyl phosphatidylserine (DOPS) is used to depict the three key molecular positions that P4-ATPases use to discriminate their substrate: i) the headgroup, ii) the glycerol backbone, and iii) the acyl chain linkages. Presented at each PL molecular position are different modifications that have been tested as P4-ATPase substrates from a variety of enzymes, with positive and negative observations indicated. Selected citations – headgroup: (Seigneuret and Devaux, 1984, Zachowski et al., 1985, Zachowski et al., 1986, Drummond and Daleke, 1995, Paterson et al., 2006, Smriti et al., 2007); backbone: (Morrot et al., 1989, Pomorski et al., 2003, Smriti et al., 2007); acyl chains: (Morrot et al., 1989, Fellmann et al., 1993, Fellmann et al., 2000, Paterson et al., 2006).