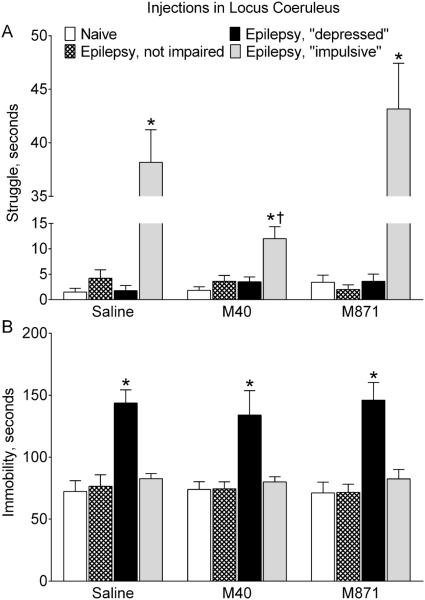
Fig. 6. Effects of galanin receptor blockers administered in the locus coeruleus on behavior.
Saline, a GalR1/GalR2 blocker M40, or a GalR2 blocker M871 were infused in LC of naïve rats (n=6 for each treatment) and epileptic animals classified as not impaired, “depressed” and “impulsive” based on their performance in the FST (see Methods). A. Effects on the struggle. Blockade of LC GalR1/GalR2 (M40) significantly shortened the duration of struggling behavior in epileptic “impulsive” rats, although the behavior was still significantly more represented than in naïve animals. Blockade of GalR2 (M871) did not modify the struggling behavior. None of GalR blockers affected the examined behavior in animals of other groups. B. Effects on the immobility. No effects on either of GalR blockers were observed in animals of all groups. Data are presented as Mean±SEM *-p<0.05 vs. Naïve in the same treatment; †- p<0.05 vs. respective category of Saline-treated rats. Two-Way ANOVA plus Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Struggle: Interaction F (6, 53) = 17.25, p< 0.0001; treatment factor F (2, 54) = 15.3 , p < 0.0001; behavior factor F (3, 53) = 146.7, p < 0.0001. Immobility: Interaction F (6, 51) = 0.1544, p = 0.9873; treatment factor F (2, 51) = 0.1423, p = 0.8677; behavior factor F (3, 51) = 35.51, p < 0.0001.