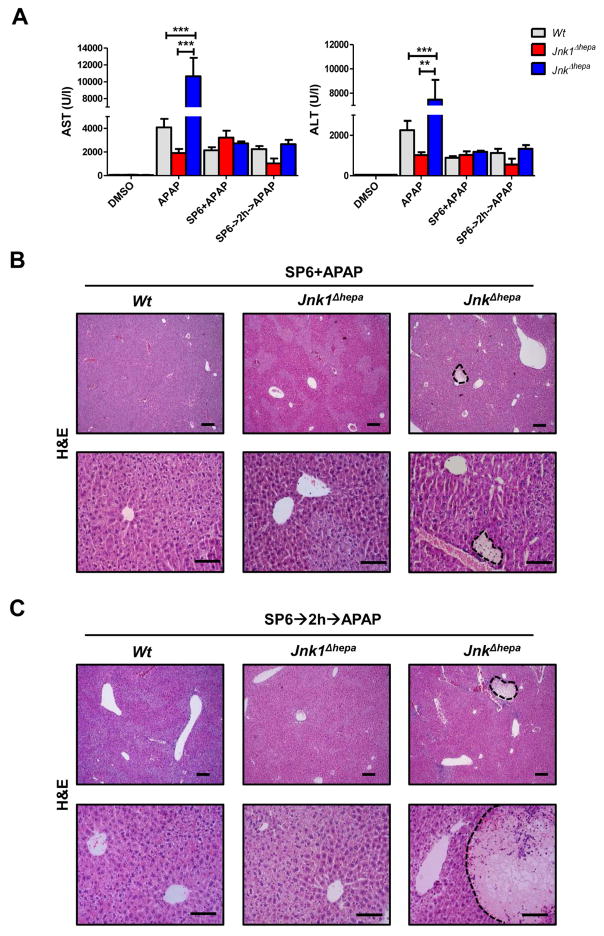
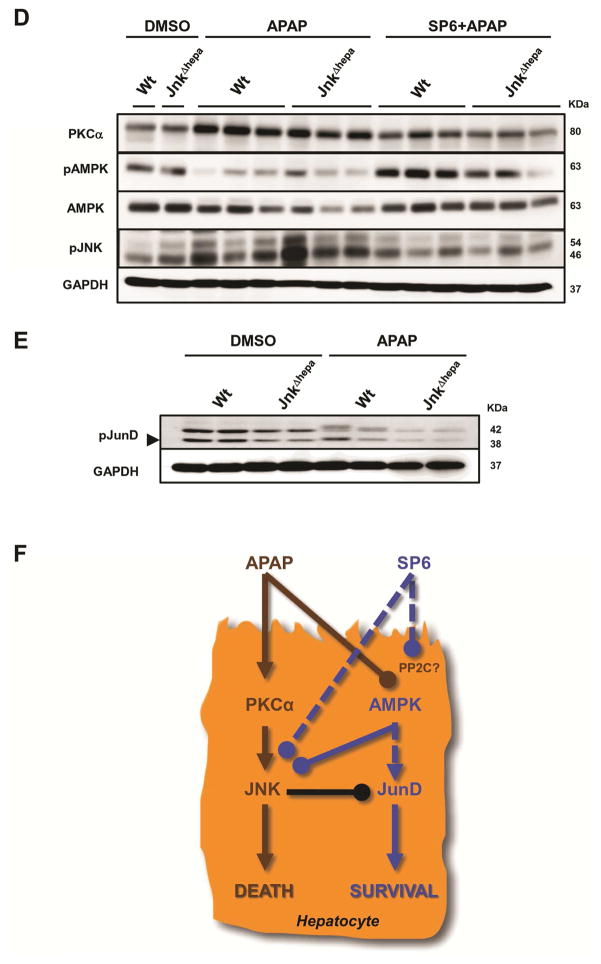
Figure 7. In vivo treatment with SP600125 suppresses APAP-induced liver injury in mice with combined JNK1 and JNK2 deletion in hepatocytes.
(A) Serum AST (left) and ALT (right) levels were determined in control (Wt), Jnk1Δhepa and JnkΔhepa mice injected with SP600125 at the same time as APAP or pre-treated with SP600125, 2h before APAP challenge. Comparison with DMSO and APAP-treated mice is shown (n=10). (B+C) Representative H&E staining of liver sections collected from the same mice sacrificed 8h after treatment and examined by an experienced pathologist. Scale bars: 50 (upper panels) and 200μm (lower panels), respectively. Dotted areas represent necrotic foci. (D) Liver extracts were collected and immunoblotting was performed, and the protein levels of PKCα, pAMPK, AMPK and pJNK determined by Western Blot. (E) Phosphorylation of JunD was performed in hepatocytic extracts. GAPDH was used as loading control. (F) APAP triggers higher PKCα, and lower AMPK – a survival pathway- expression inducing JNK phosphorylation and cell death. The JNK classical inhibitor SP600125 exerts an off- target effect by facilitating phosphorylation of AMPK and preventing JNK phosphorylation in hepatocytes.