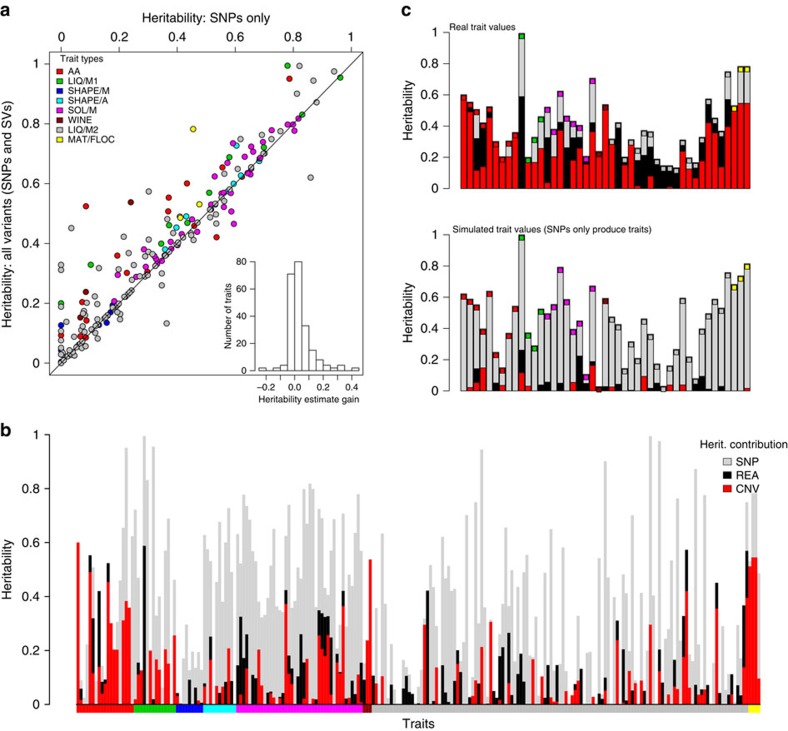
Figure 4. SVs contribute to quantitative traits.
(a) Heritability estimates are improved by the addition of SVs. Heritability estimates for 228 traits (Supplementary Table 5), using only SNP data (x axis) range from 0 to 96% (median 29%). Adding SV calls (y axis) increases the estimates (median 34%), with estimates for some traits being improved up to a gain of 43% (histogram inset). The diagonal line shows where estimates after adding SVs are the same as those without (x=y). Inset: the distribution of the ‘gain’ in heritability after adding SV calls (median 0.4%, maximum 43%). Points are coloured by trait types, according to legend top left. (b) The contributions of SNPs (grey), CNVs (red) and rearrangements (black) to heritability varied considerably between traits. Coloured bars along the x axis indicate the trait types. heritability estimates are in Supplementary Table 5. The panel below bars indicates trait types as in the legend for part (a). (c, top) For some traits, SVs explained more of the trait variation than SNPs. Boxes are coloured as legend in a. (c, lower) Analysis of simulated data generated with assumption that only SNPs cause traits indicates that the contribution of SVs to trait variance is unlikely to be due to linkage. Traits from left are; with red inset at top, free amino acid concentrations (glutamine, histidine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline and tyrosine), with green inset liquid media growth traits (maximum mass in minimal media, time to maximum slope, most rapid slope and highest cell density in rich media), in with magenta inset colony growth on solid media (with Brefeldin, CuSO4, H2O2, hydroxyurea, 0.0025% MMS, 0.005% MMS, with proline and 0.001% SDS), wine traits with Burgundy inset (malic acid accumulation and glucose+fructose ultilisation), with grey inset liquid media conditions (caffeine lag, rate and efficiency, CsCl12 efficiency, diamide growth rate, EMS growth rate, ethanol efficiency, ethanol growth rate, galactose growth rate, growth rate at 40°C, HqCl2 lag, KCl efficiency, MgCl2 efficiency, MMS lag, NiCl lag, unstressed lag and rate, SrCl efficiency, tunicamycin lag and rate), and with yellow insets mating traits (the proportion of free spores, mating figures observed and total spore counts).