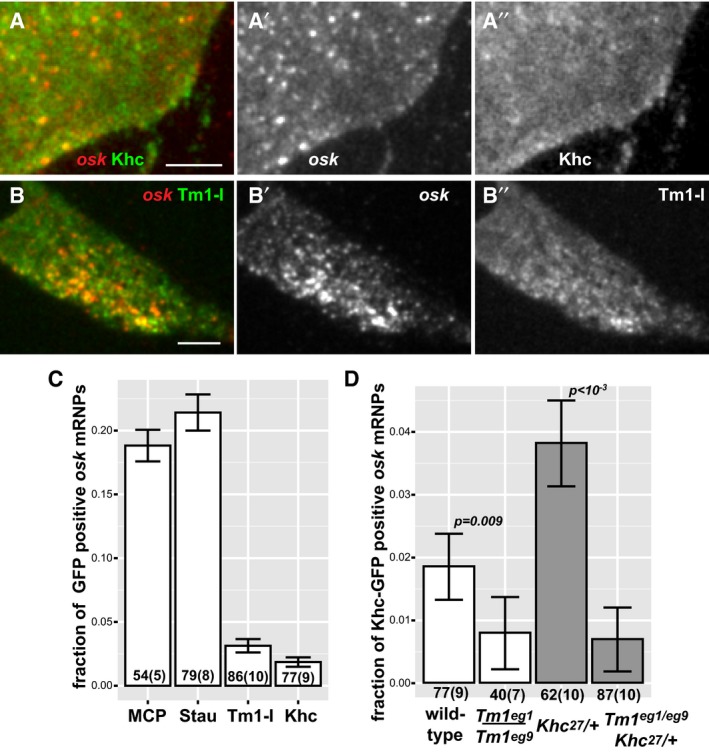
Figure 2. Composition of oskar mRNPs ex vivo .
-
A–B″Colocalization of oskMS2‐mCherry (red, A, B) (A′, B′) with Khc‐EGFP (green, A) (A′) or with EmGFP‐Tm1‐I (green B) (B′) in ex vivo ooplasmic preparations. Scale bars represent 5 μm.
-
CFraction of oskMS2‐MCP‐mCherry mRNPs located non‐randomly within a 200 nm distance of one of the indicated GFP‐tagged protein particles in ex vivo ooplasmic preparations. MCP indicates MCP‐EGFP which, like MCP‐mCherry, can bind to MS2 loops. Staufen (Stau) is a dsRNA binding protein and bona fide partner of oskar mRNA (St Johnston et al, 1991, 1992). All values are significantly different from zero (P < 10−3, one‐sample t‐test).
-
DFraction of oskMS2‐mCherry mRNPs colocalizing (max. 200 nm) non‐randomly with Khc‐EGFP particles in wild‐type and Tm1 eg1/Tm1 eg9 ooplasms in the presence of two (white) or one (grey) copy of endogenous Khc.
