-
A
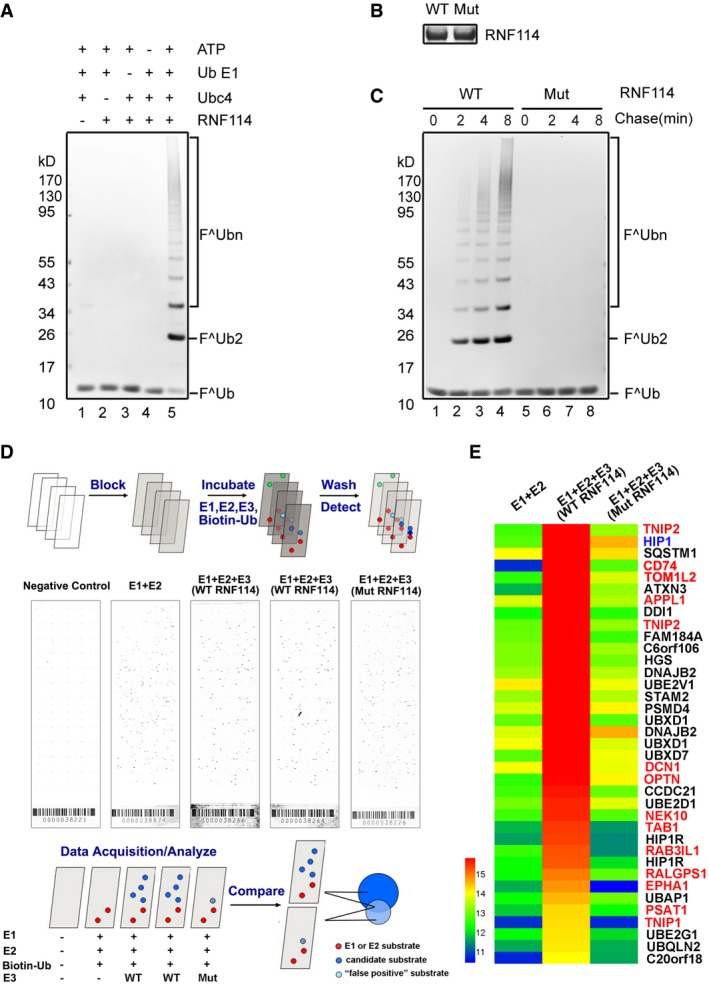
In vitro ubiquitination assay. Purified His‐RNF114 was subjected to ubiquitination assays with the indicated components, and the samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti‐FLAG (Ub) antibody. Lanes 1–4 indicate negative controls. The results show that recombinant RNF114 efficiently catalyzed the formation of polyubiquitin chains.
-
B, C
Purified wild‐type and RING‐mutated His‐RNF114 were stained by Coomassie blue (B). Purified wild‐type and RING‐mutated His‐RNF114 were subjected to ubiquitination assays together with E1, Ubc4, FLAG‐Ub, and ATP. The results show that mutant RNF114 lacked ubiquitination activity (C).
-
D
Screening for proteins ubiquitinated by RNF114 on a proteome array. Putative substrates of RNF114 were identified on Ubiquitin Ligase Substrate Identification on ProtoArray® Human Protein Microarrays v5.0. Ubiquitination reactions were performed on quintuplicate arrays using the indicated components, the five sub‐array are, respectively, negative controls, E1 + E2 (no E3), WT RNF114 (two arrays, duplicate), and mutated RNF114.
-
E
A heat map comparing hits between E1 + E2, E1 + E2 + WT RNF114, and E1 + E2 + mutated RNF114 reactions. Candidate substrates of RNF114 selected for further characterization are indicated in red font; HIP1, indicated by blue font, was considered to be a false positive because it was also detected in the mutated RNF114 reaction. Black font indicates proteins with ubiquitin‐binding domains such as UIM, UBA, or CUE or proteins without clearly reported functions, which were excluded from further investigation.