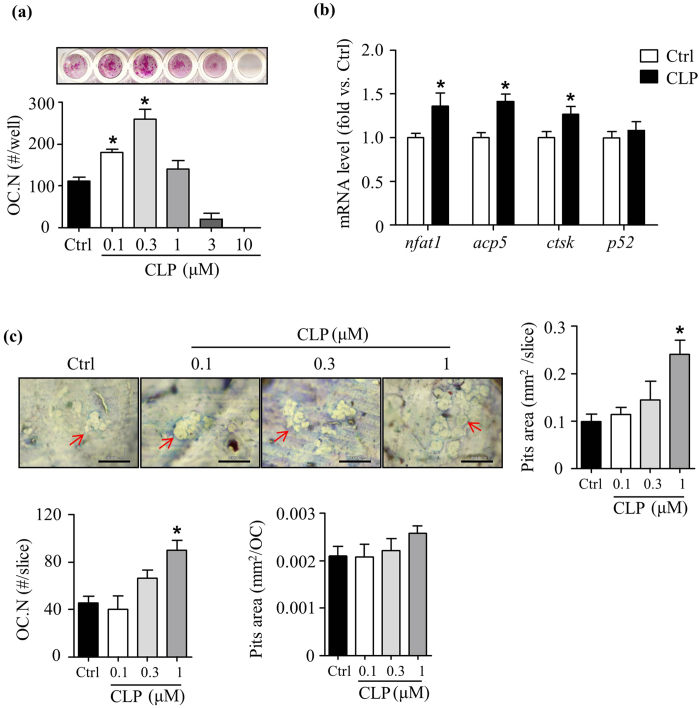
Figure 3. Clomipramine increases osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vitro.
. Bone marrow cells from WT mice were used. (a) Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of CLP in the presence of RANKL and M-CSF for 7 days in OC formation assays. Cells were stained for TRAP activity. TRAP+ OC number was assessed. Values are mean ± S.D. of 4 wells/treatment. Experiments = 3. (b) Cells were cultured with RANKL and M-CSF and treated with CLP (0.3 μM) for 7 days. The expression levels of OC-related genes were determined by qPCR. Fold changes in relative gene expression were calculated in relation to expression levels in Ctrl. Experiments = 3. (c) Bone resorption assays were performed by culturing cells on bone slides for 10 days using the same culture conditions, as in (a). TRAP staining was performed for counting OC number. OCs on bone slices were then removed and followed by toluidine blue staining for measuring resorption pits. Bar graphs showing pits area and OC number per bone slice, and pits area per OC, respectively. Values are mean ± S.D. of 4 bone slices. Experiments = 3. *p < 0.05 versus Ctrl. Ctrl: PBS, CLP: Clomipramine. Scale bars: 100 μm in (c).