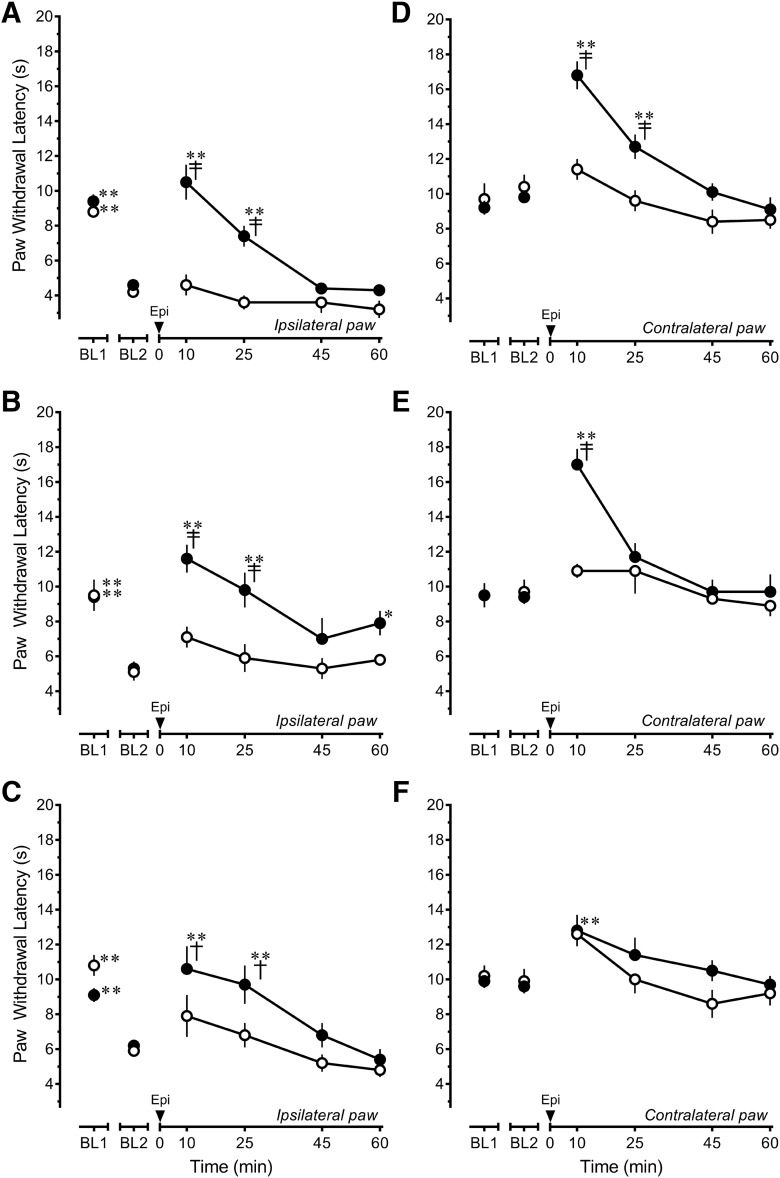
Fig. 3.
The antihyperalgesic effect of epibatidine persists, whereas its antinociceptive effect declines in a time-dependent manner after peripheral inflammatory injury. Epibatidine (Epi; 4.11 ng, ●) or saline (○) was microinjected in the rostral ventromedial medulla of rats 4 h (A, D; saline n = 4, epibatidine n = 10), 4 d (B, E; saline n = 5, epibatidine n = 8), or 2 weeks (C, F; saline n = 6, epibatidine n = 11) after intraplantar injection of CFA in the left hind paw. A–C, Ipsilateral, inflamed hind paw. D–F, Contralateral, uninflamed hind paw. Data are mean ± SEM. BL1 refers to paw withdrawal latency before and BL2 refers to paw withdrawal latency after injection of CFA. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with BL2 values. †p < 0.05, ‡p < 0.01 compared with saline control at the corresponding time point. Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Holm–Sidak test.