Fig. 5.
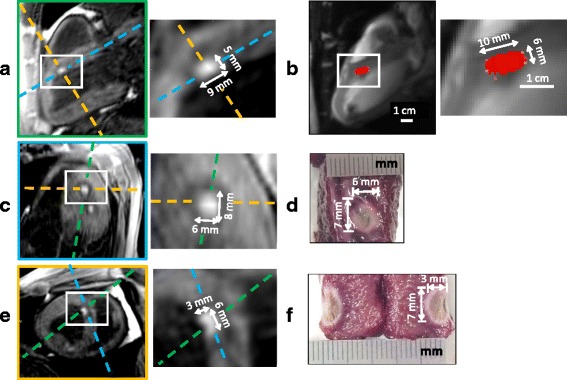
Comparison of lesion dimensions of one representative RFA between post-ablation T1-w 3D images (a, c and e), real-time TD map (b) and macroscopic observations with TTC staining (d and f). Cumulative TD was computed in real-time simultaneously to a RFA of 60 s at 60 W (RFA #4 on sheep #2), given the TD map (b) at the end of the procedure. After the ablation, a 3D T1-w IR volume was acquired and the created lesion could be visualized in hyper signal compared to the surrounding tissue attributed to edema. To compare 2D TD map and 3D-IR lesion sizes, the equivalent 2D slice was reconstructed from the 3D T1-w volume, resulting in the image (a, green dashed line perpendicular to other views c and e) with the same position, orientation and zoom than (b). After the intervention, the animal was euthanized and the heart was dissected to expose the lesion. The macroscopic view from the endocardium side is shown in (d) and the equivalent slice (c) was reconstructed from the 3D T1-w volume (blue dashed line perpendicular to other views a and e). The lesion sample was finally cut to expose the extent in depth in the myocardium (f) and the equivalent slice (e) was reconstructed from the 3D T1-w volume (yellow dashed line perpendicular to other views a and c)
