FIG 1.
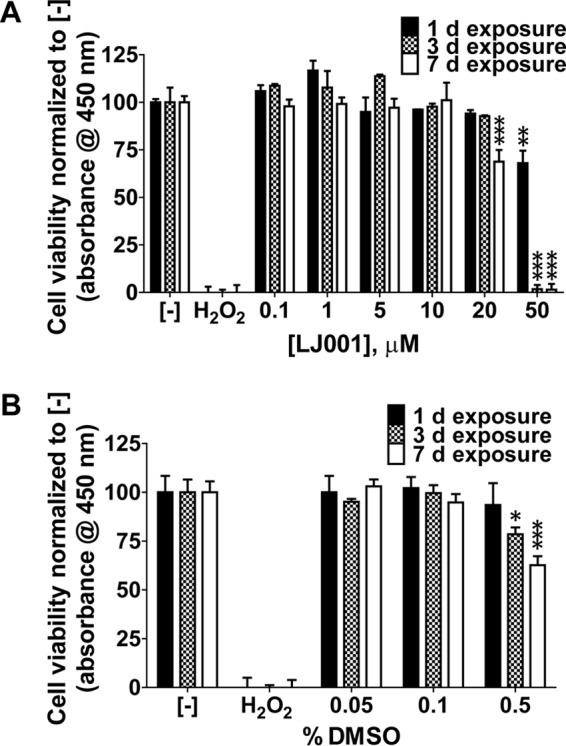
LJ001 is not cytotoxic at antiviral concentrations. EPC cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of LJ001 (A) or the vehicle control (DMSO) (B) for 1, 3, and 7 days in the presence of light at the time of addition. Formazan dye absorbance was measured at 450 nm. Positive-control wells were exposed to hydrogen peroxide (40 mM final concentration) for 1 day. The negative control (−) is no drug exposure. (A) Exposure to 0 to 50 μM LJ001 (50 μM LJ001 with 0.5% DMSO, 10 μM LJ001 with 0.1% DMSO, and 1.0 μM LJ001 with 0.01% DMSO). There was no cytotoxicity to EPC cells at up to 10 μM LJ001. Toxicity occurred when cells were exposed to 20 μM LJ001 for 7 days and 50 μM LJ001 at all time points. Data represent mean cell viabilities ± standard errors (n = 3) normalized to values for no treatment (negative control). **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (B) Exposure to 0 to 0.5% DMSO. No cytotoxic effects were observed at concentrations of up to 0.1%. Cytotoxic effects were detected after exposure to 0.5% DMSO at 3 and 7 days. Data represent mean cell viabilities ± standard errors (n = 3) normalized to values for no treatment. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.
