FIG 5.
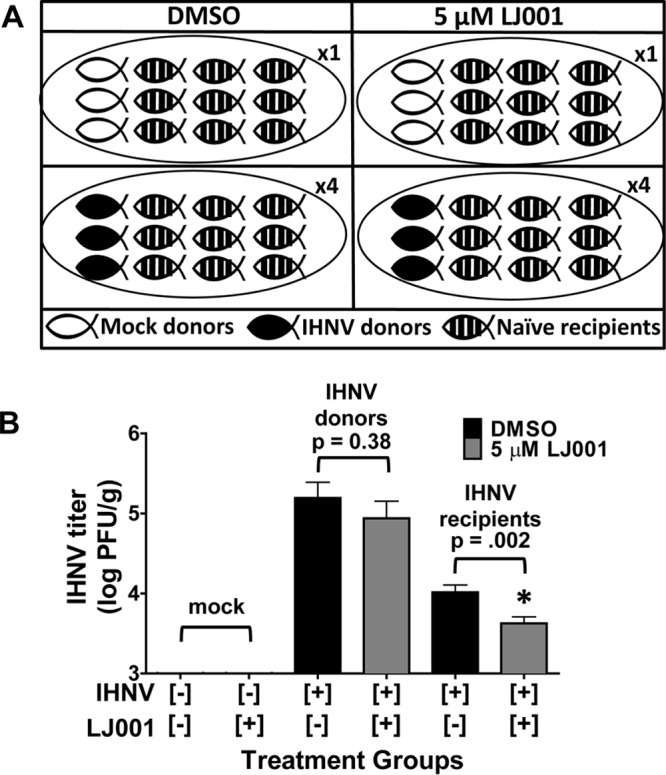
LJ001 inhibits horizontal transmission of IHNV. Rainbow trout were immersion infected with 2 × 105 PFU/ml IHNV (donor fish) or MEM (mock) and remained in the flowthrough for 24 h. (A) Experimental groups. Three IHNV- or mock-infected donor fish were placed into static challenge containers, followed by the addition of LJ001 (5 μM final concentration) or 0.005% DMSO (vehicle control); after 15 min, nine naive recipient fish were added to each challenge container for cohabitation (n = 1 challenge container per mock-infected group, and n = 4 challenge containers per IHNV-infected group). Water exchanges and fresh LJ001 or DMSO dosing occurred every 24 h. (B) For donor fish that were immersion infected with IHNV, there was a nonsignificant (P = 0.38, as determined by Student's t test) decrease in viral loads for the LJ001-treated donor fish (12 fish) compared to DMSO-treated (vehicle control) donor fish (12 fish). There was a significant decrease in viral loads for LJ001-treated IHNV recipient fish (36 fish) compared to DMSO-treated (control) IHNV recipient fish (36 fish) (P = 0.002). All mock-infected fish had negative titers. Data represents mean IHNV titers ± standard errors (n = 12 for mock groups, n = 12 for IHNV donors, and n = 36 for IHNV recipients).
