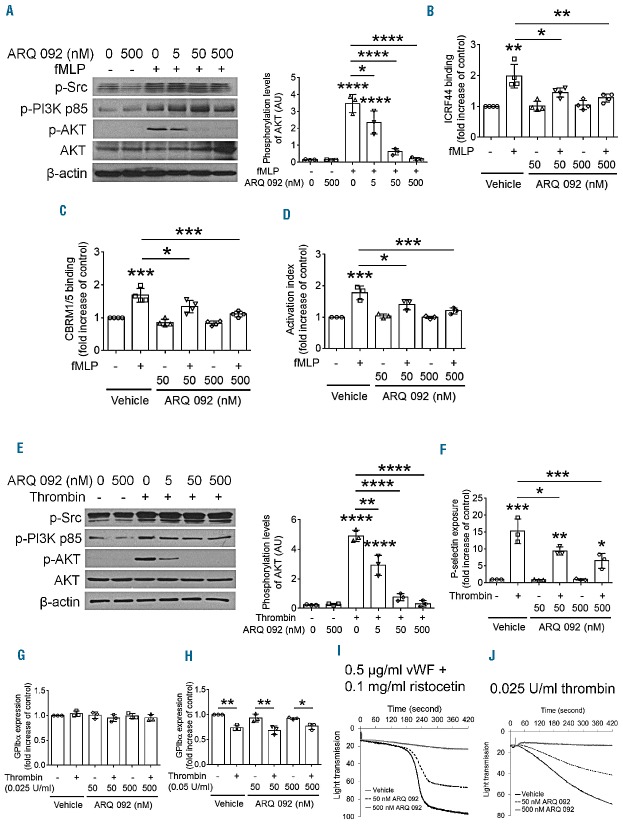
Figure 1.
ARQ 092 inhibits activation of neutrophils and platelets isolated from SCD patients in vitro. (A–D) Neutrophils or (E–J) platelets isolated from SCD patients were pretreated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO), or 50 or 500 nM ARQ 092 and then incubated with or without 0.5 μM fMLP or 0.025 U/mL thrombin for 2 min, respectively. (A) Immunoblotting was performed using equal amounts (50 μg) of neutrophil lysate protein, followed by densitometry (n = 3). (B–D) Flow cytometry was performed using phycoerythin-conjugated control IgG or antibodies against total (ICRF44) or activated αMβ2 (CBRM1/5), or DyLight 488-conjugated fibrinogen. The geometric mean fluorescence intensity of antibodies was normalized to that of control IgG, and data are presented as fold increase compared with vehicle-treated, unstimulated cells. (E) Immunoblotting was performed using equal amounts (50 μg) of platelet lysate protein, followed by densitometry (n = 3). (F) Flow cytometry was performed to measure P-selectin exposure. (G–H) Platelets were stimulated with (G) 0.025 or (H) 0.05 U/mL thrombin. The surface amount of GPIbα was measured by flow cytometry. (I) Platelet agglutination was induced by 0.5 μg/mL vWF and 0.1 mg/mL ristocetin. (J) Platelet aggregation was induced by 0.025 U/mL thrombin. The representative agglutination or aggregation trace was obtained from three independent experiments. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3–4). *P<0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P<0.001, and ****P<0.0001 versus unstimulated vehicle control (or between two groups), ANOVA and the Tukey test.