Figure 3.
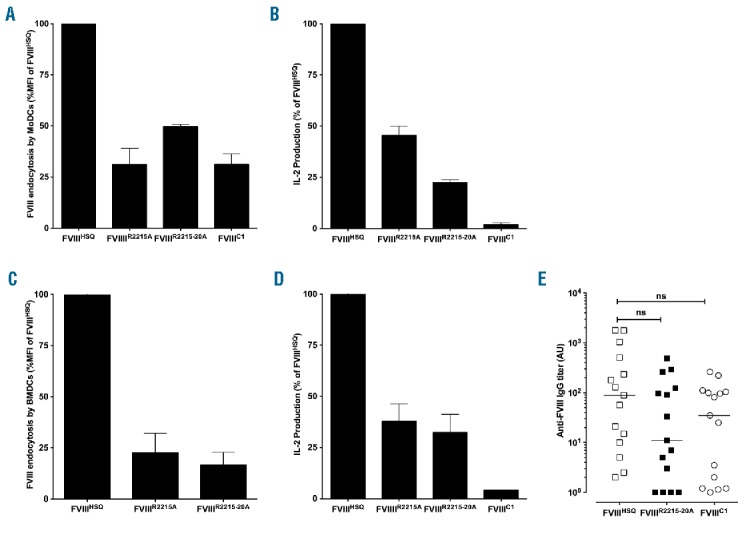
domain mutations alter FVIII endocytosis and presentation by APCs, but do not alter FVIII immunogenicity in vivo. B domain-deleted wild-type FVIII (FVIIIHSQ) or the mutants FVIIIR2215A, FVIIIR2215-20A or FVIIIC1 were added at 20 nM to MoDCs (Panel A) or BMDCs (Panel C) for 30 min. Internalized FVIII was detected as described in Methods. Results are expressed as the percentage of MFI, whereby 100% corresponds to MFI obtained with FVIIIHSQ. Panels B and D represent activation of a FVIII-specific HLA-DRB1*0101-restricted T-cell hybridoma by B domain-deleted FVIII-loaded (10 nM) HLA-matched human MoDCs or splenocytes from SURE-L1 mice, respectively. Supernatant was collected after 24 hr and the IL-2 produced by the activated T cells was measured. Representative of three experiments (mean±SEM). Panel E. FVIII-deficient mice were injected intravenously once weekly for 4 weeks with 1 μg of B domain-deleted FVIIIHSQ, FVIIIC1 or FVIIIR2215-20A. One week after the last injection, blood samples were collected. Anti-FVIII IgG titers are defined as arbitrary units based on standard curves generated using mAb6. Statistical significances were assessed using the two-tailed nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test. ns: not significant; FVIII: factor VIII; MoDCs: monocyte-derived dendritic cells; A.U.: arbitrary unit; IL-2: interleukin-2; IgG: immunoglobulin G; MFI: median fluorescence intensity; BMDCs: bone marrow-derived dendritic cells.
