Figure 1.
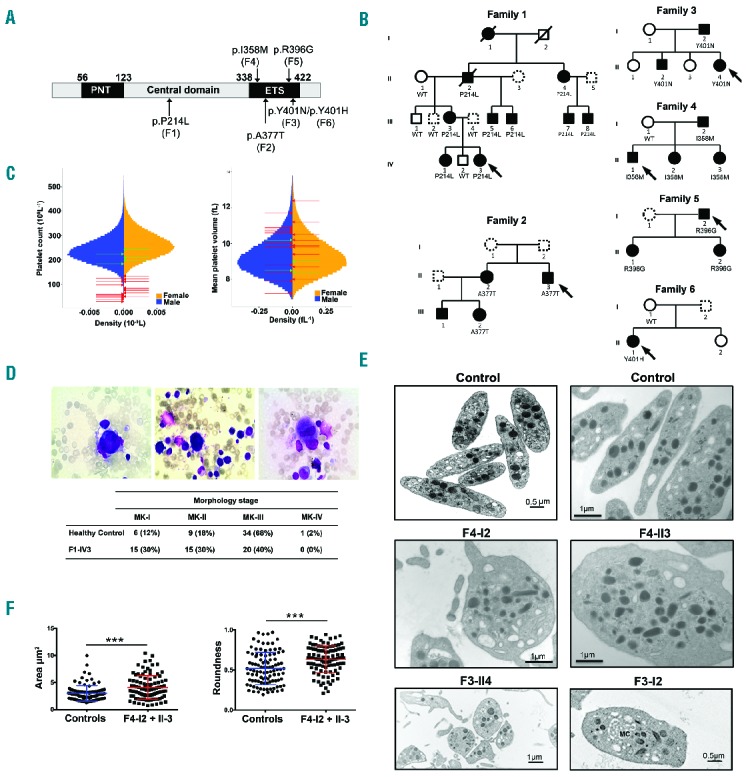
Identification of variants in ETV6 underlying AD thrombocytopenia, megakaryocyte and platelet characteristics. (A) Schematic representation of the different domains of the ETV6 protein. The N-terminal domain (PNT), central domain and C-terminal domain containing a DNA-binding domain (ETS) are depicted. Arrows indicate the location of the ETV6 variants and the corresponding family is mentioned in brackets. (B) Pedigrees for the affected families. Squares denote males, circles denote females and slashes represent deceased family members. Black filled symbols represent thrombocytopenic family members and dotted line symbols represent non-tested members. The families F1, F2, F3, F4, F5 and F6 carried the ETV6 p.P214L, p.A377T, p.Y401N, p.I358M, p.R396G and p.Y401H variants, respectively, which segregated with thrombocytopenia. See Table 1 for blood cell count values. (C) Sex-stratified histograms of platelet count and mean platelet volume measurements, obtained using a Coulter hematology analyzer, from 480,001 UK Biobank volunteers, after adjustment for technical artifacts. The red arrows superimposed upon the histograms indicate the sex and values for patients with a deleterious variant in ETV6. The green arrows indicate the sex and values for relatives homozygous for the corresponding wild-type allele. (D) BM smears (May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining) from family F1 propositus (F1-IV3). Left: a relatively immature MK with reduced cytoplasm. Middle: a micromegakaryocyte without granules, with immature cytoplasm (basophilic) and nucleus. Signs of impaired proplatelet formation can be observed. Right: a mature MK of reduced size with a hypolobulated nucleus. Table 1 indicates the % of MKs at each stage of maturation in the BM samples from family F1 proposita (F1-IVI3) and a healthy control. (E) Ultrastructural aspects of platelets from patients F3-I2 and F3-II4, F4-I2 and F4-II3 and unrelated healthy controls. Upper panel: aspect of healthy platelets; middle panel: series of mostly rounder platelets from patients F4-I2 and F4-II3, lower panel: a series of platelets emphasizing anisocytosis in patient F3-114 and a platelet from patient F3-I2 with abnormal membrane complex (MC). Note the heterogeneous presence of α-granules with an occasional granule of increased size. (F) The platelet area and roundness was quantified. Perfect round platelets would have a value of 1. Values are the means and SD as quantified for 50 randomly selected platelets per subject using two-tailed unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. ***P<0.0001. WT: wild-type; MK: megakaryocyte; PNT: pointed; ETS: ET6 transformation-specific.
