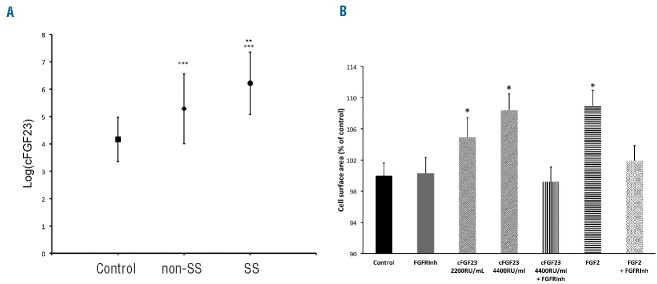
Figure 1.
(A) Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) concentration in patients in sickle cell disease (SCD) and controls. C-terminal FGF23 (cFGF23) plasma concentration is higher in SCD patients with SS (circle) or non-SS (diamond) genotype than in control subjects (square). cFGF23 concentration was natural Log-transformed to obtain normal distribution. Anova P<10−4. Differences between groups were analyzed with Tukey-Kramer’s test: **P=0.0002 SS versus non-SS; ***P<10−4 versus control. (B) C-terminal FGF23 (cFGF23) induces adult rat ventricular cardiomyocyte (ARVMs) hypertrophy. cFGF23 induces cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in a dose-dependent manner. cFGF23-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy is abolished by the FGFR inhibitor (PD166866). FGF2 was used as a control. ARVMs in culture were treated for 24 hours with cFGF23, or FGF2, or with control medium. N=5–9 preparations. Anova P<0.0001. Comparison to control *P=0.005 Dunnet test.