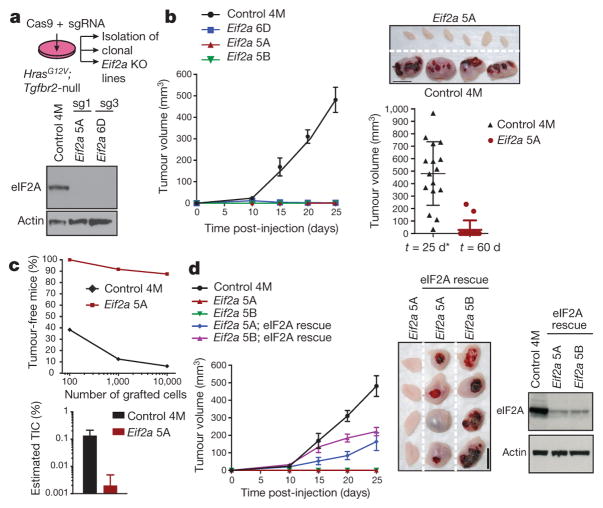
Figure 5. eIF2A controls tumour formation.
a, HrasG12V;Tgfbr2-null SCC keratinocytes were infected with lentiviruses containing Cas9 and sgRNAs to establish Eif2a-knockout (KO) and non-targeting control lines. Western blot confirms Eif2a ablation by two different sgRNAs (sg1 and sg3). 4M denotes control clone; 5A, 5B and 6D denote Eif2a knockout clones. b, Eif2a ablation abrogates tumour growth. Plotted is mean tumour volume ± s.e.m. after subcutaneous injection of 105 cells (n =16 control, n = 14 knockout clone 5A, n = 12 clones 5B and 6D). Representative tumours 25 days after injection are shown. Asterisk denotes terminated owing to tumour size. Scale bar, 1 cm. c, Limiting dilution assay. Graphs show percentage of tumour-free mice 4 weeks after injection and estimated tumour-initiating cells (TIC) (n = 24 grafts per dilution and genotype). d, Re-introducing eIF2A by pCMV-Eif2a transformation rescues Eif2a-knockout defective tumour initiation. Western blot confirms eIF2A restoration. Data are mean ±s.e.m. (n =16 control, n = 14 clone 5A, n =12 clone 5B, n = 16 clone 5A; pCMV::Eif2a, n = 16 clone 5B; pCMV::Eif2a). Scale bar, 1 cm.