FIGURE 1.
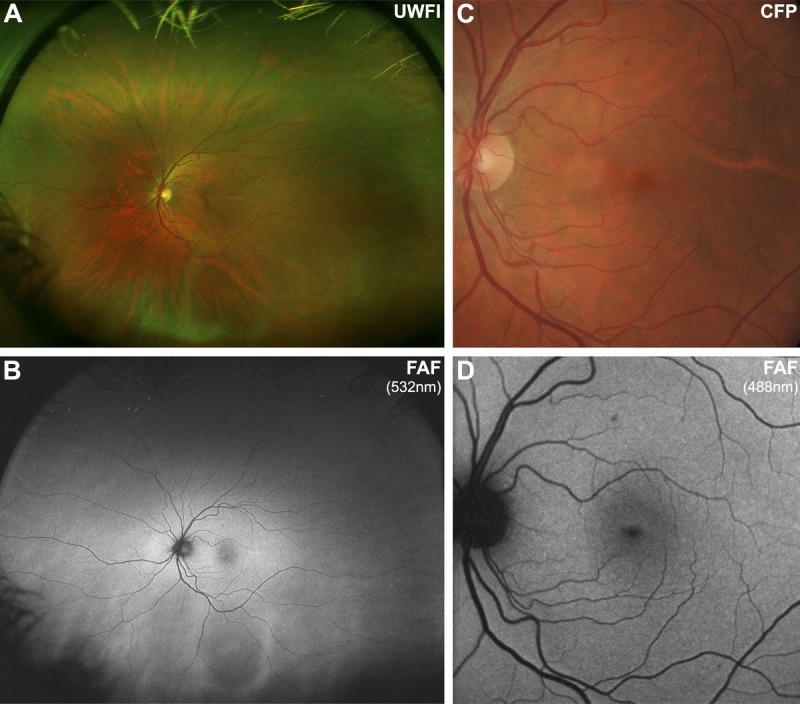
Imaging results from a 43-year-old Caucasian female with a normal macula. Note that the normal fundus displays diffuse, homogenous autofluorescence with large retinal blood vessels and the optic disc appearing as shadows of hypo-autofluorescence. The central macula shows a gradual reduction in autofluorescence approaching the fovea, due to macular pigment. A, Optomap composite ultra-widefield image representing approximately 200 degrees of the fundus. B, Corresponding ultra-widefield fundus autofluorescence (FAF) image showing the potential of this device to detect more widespread disease than narrower fields. C, Retinal photograph cropped to size. D, FAF image obtained using the Heidelberg Retinal Angiograph 2 with a 30-degree field of view, which was the primary method of image acquisition in 49/64 articles included in this review. UWFI, ultra-widefield image; FAF, fundus autofluorescence; CFP, color fundus photograph.
