Fig. 1.
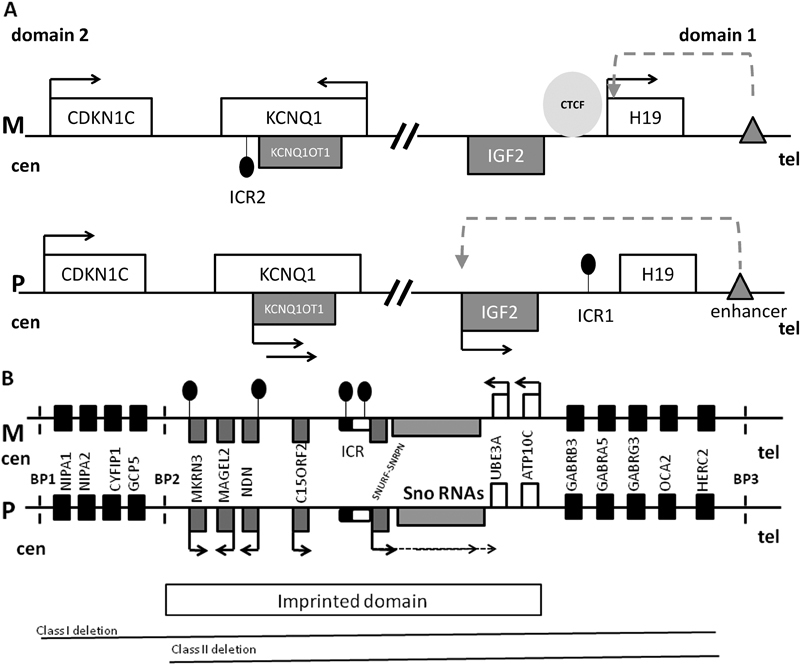
( A ) The map of chromosome 11p15.5 imprinted cluster consisting of domain 1 and 2. M is maternal chromosome, P is paternal chromosome, cen is centromere, tel is telomere, white rectangles are maternally expressed genes, gray rectangles are paternally expressed genes, black arrows indicate gene expression, black circles indicate DNA methylation, gray triangle is enhancer, dashed arrow indicates accessibility of IGF2 promoter to the enhancer, and light gray circle is CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF). In domain 1, imprinting control region 1 (ICR1) is located upstream of H19 noncoding RNA and is methylated on the paternal allele. Methylation prevents CTCF binding to the paternal ICR1, permitting access of the IGF2 promoter to the downstream enhancer. Thus, IGF2 is expressed, whereas H19 is silenced. On the maternal allele, CTCF binds to the unmethylated ICR1, blocking IGF2 promoter access to the enhancer. Thus, IGF2 is silenced and H19 uses the enhancer and is transcribed. In domain 2, ICR2 is located at the 5′ end of the noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 (KCNQ1 opposite strand transcript) and is methylated on the maternal allele. When ICR2 is unmethylated, KCNQOT1 is transcribed, KCNQ1 and CDKN1C are silenced in cis . Methylation of ICR2 results in KCNQOT1 silencing and expression of KCNQ1 and CDKN1C. IGF2 promotes growth, and CDKN1C suppresses growth. Overexpression of IGF2 and/or loss of expression of CDKN1C is associated with Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome (overgrowth), whereas overexpression of CDKN1C and/or loss of expression of IGF2 is associated with Russell–Silver syndrome (growth restriction). ( B ) Map of human chromosomal region 15q11-q13 involved in Prader-Willi (PWS), Angelman (AS), and 15q11q13 maternal duplication syndromes, containing an imprinted domain as well as biallelically expressed genes. M is maternal chromosome, P is paternal chromosome, cen is centromere, tel is telomere, white rectangles are maternally expressed genes, gray rectangles are paternally expressed genes, black arrows indicate gene expression in a parent of origin-specific manner, and black rectangles are biallelically expressed genes. Imprinted control region (ICR) is shown as rounded rectangle with the black half being the PWS critical element and the white part the AS critical element; black circles indicate DNA methylation. SNURF/SNRPN gene expression is regulated by ICR methylation and it is expressed in multiple splice forms, including the UBE3A antisense transcript which is paternally expressed in brain and silences paternal UBE3A transcription in brain. Clusters of C/D box small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are encoded within introns of SNURF-SNRPN and are regulated by its promoter. Promoters of MKRN3 and NDN are methylated on the maternal allele. Dashed vertical lines show the regions of common break points (BP) located within regions of low copy repeats. The most common causes of PWS and AS are paternal and maternal deletions, respectively, occurring between BP1 and BP3 or between BP2 and BP3. It is known that the critical gene for AS is UBE3A which is expressed from the maternal allele in human brain and biallelically in other tissues. The relative contributions of single genes to PWS and maternal 15q11-q13 duplication syndrome remain unknown. The drawing is not to scale.
