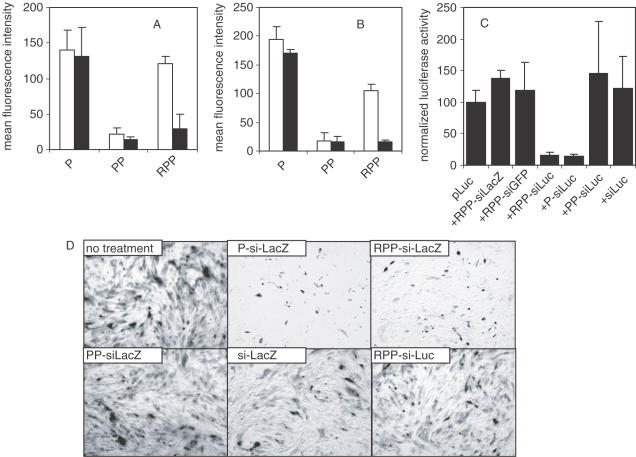
Figure 3.
In vitro activity of siRNA nanoplex. (A and B) siRNA nanoplex binding to cells. 1 × 105 HUVEC (A, open bars) or N2A cells (B, open bars) were incubated with 2 μg fluorescently labeled siRNA formulated in P-, PP- or RPP-nanoplexes for 1 h at 4°C. Both cell types express integrins. After the incubation period, the cells were washed, fixed with 4% buffered formaldehyde and cell-bound fluorescence analyzed by FACS analysis. Unshielded positively charged P-nanoplexes showed relatively high cell binding to both cell types. Shielding of the charged nanoplex with PEG (PP-nanoplexes) reduced cell interaction, which was restored by coupling of the RGD peptide to the distal end of the PEG-shield (RPP-nanoplexes). Pre-incubation of HUVEC (A, closed bars) or N2A (B, closed bars) with a 100-fold molar excess of RGD peptide reduced binding of RPP-nanoplexes while leaving binding of P-or PP-nanoplexes unaffected, indicating that the binding of RPP-nanoplexes to cells is mediated by the RGD peptide targeting ligand. (C) Luciferase silencing in vitro. N2A cells were transfected with 2 μg luciferase plasmid, using cationic lipids without siRNA or cotransfected with 1 μg siRNA formulated as RPP-siLacZ, RPP-siGFP, RPP-siLuc, P-siLuc, PP-siLuc or free siLuc. Sequence-specific silencing of luciferase expression with siLuc is observed for RPP- and P-nanoplexes. Luciferase activity of cells treated with various agents were normalized assuming the activity of cells transfected with luciferase plasmid to be 100%. (D) β-Galactosidase silencing in vitro. SVR-bag 4 endothelial cells, constitutively expressing β-galactosidase were left untreated or incubated with 10 μg of siRNA as follows: P-siLacZ, RPP-siLacZ, PP- siLacZ, RPP-siLuc or free siLacZ. After 3 h incubation, the cells were washed and 48 h after transfection, the cells were stained for β-galactosidase activity. Only panels P-siLacZ and RPP-siLacZ show clear inhibition of β-galactosidase expression.