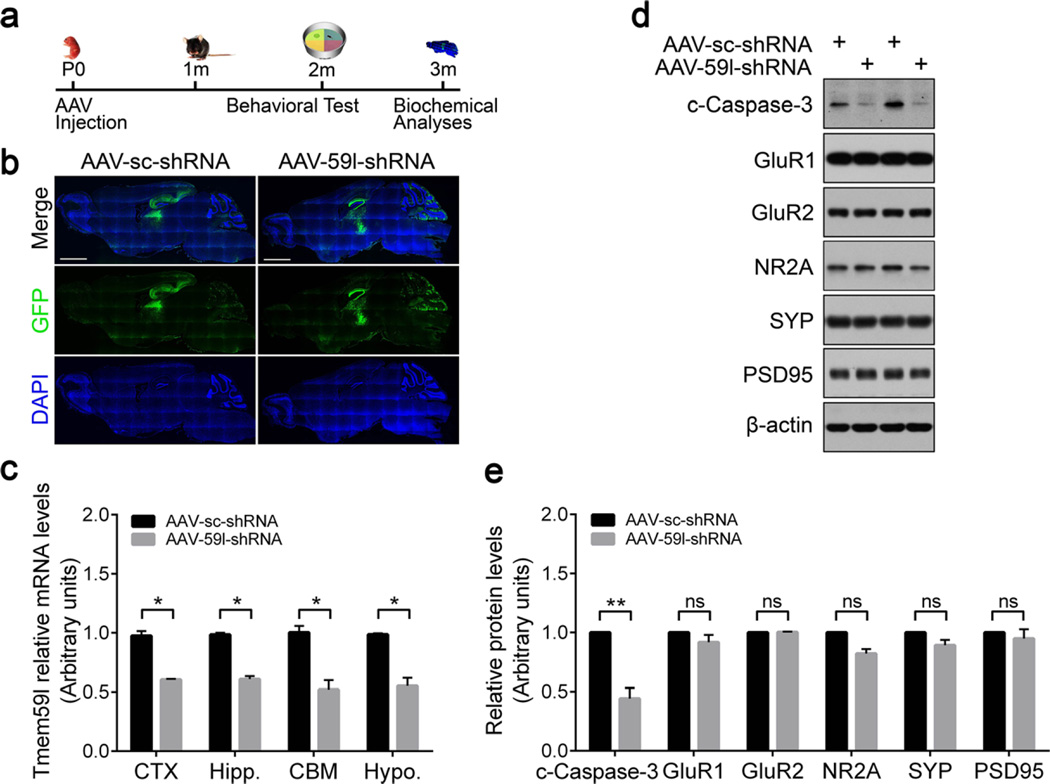
Fig. 6.
AAV-mediated knockdown of TMEM59L reduces the activation of caspase-3 in mice. a The workflow of stereotactic AAV injection experiment. C57BL/6 mice at P0 were bilaterally injected with AAVs expressing Tmem59l shRNA (AAV-59l-shRNA) or a scrambled shRNA (AAV-sc-shRNA) into the cerebral ventricle. Mice were then subjected to behavioral analyses at 2 m of age and sacrificed at 3 m of age for biochemical analyses. b Representative EGFP fluorescence images of whole mouse brain sections after AAV injection. Scale bar, 2000 µm. c Total RNAs were extracted from cerebral cortex (CTX), hippocampus (Hipp.), cerebellum (CBM), and hypothalamus (Hypo.) regions of mice injected with AAV for 3 months, reverse transcribed, and then subjected to qRT-PCR. The mRNA levels of Tmem59l were normalized to those of β-actin and compared to those of controls (set as one arbitrary units). n = 4, *p < 0.05. d Indicated proteins from hippocampus lysates were analyzed by Western blot and e quantified by densitometry for comparison. n = 4; ns, not significant, **p < 0.01