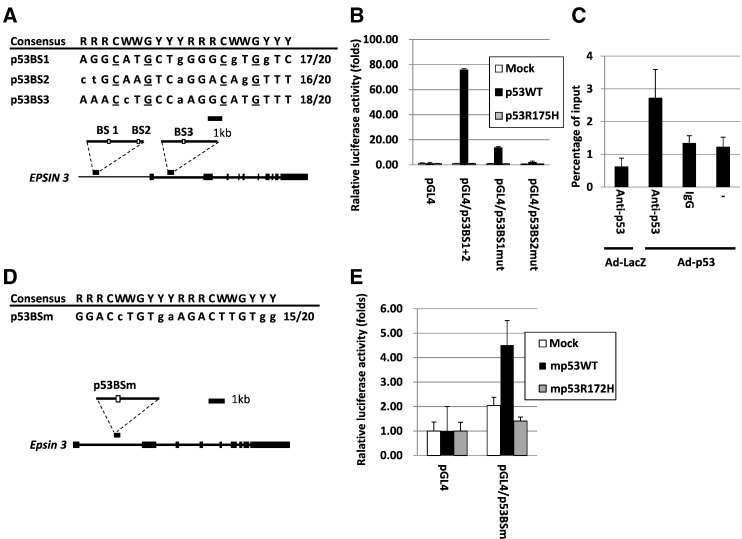
Figure 2.
(A, D) White boxes indicate the location of the potential p53 binding sequences (p53BS1, p53BS2, p53BS3 and p53BSm). Comparison of these potential binding sequences to the consensus p53 binding sequence. R, purine; W, A or T; Y, pyrimidine. Nucleotides identical to the consensus sequence are in capital letters. The underlined cytosine and guanine residues were substituted for thymine to examine the specificity of the p53 binding sequence. (B, E) Results of the luciferase assay of the genomic fragments containing p53BSs with or without amino acid substitutions at the p53BSs. The luciferase activity is indicated relative to the activity of the mock vector with S.D. (n = 3). Mutant p53 represents the plasmid expressing either human p53 with a missense mutation (R175H) or mouse p53 with a missense mutation (R172H) (C). U373 MG cells were used for these analyses.