FIGURE 2.
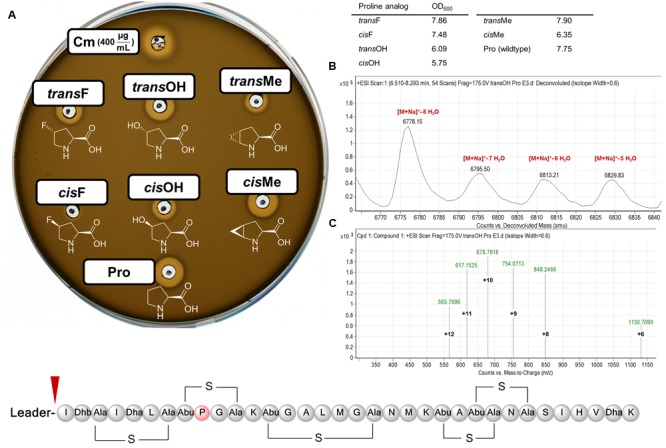
Modification of nisin with ncAAs. (A) Antimicrobial activity assay using novel nisin variants produced by recombinant expression and SPI using ncAA analogs of proline. E. coli expression samples (harvested cell densities tabulated as OD600) were normalized and tested for inhibition of the Gram-positive indicator strain L. lactis NZ9000 carrying plasmid pNG nisPT for cleavage of the AMP leader (Khusainov and Kuipers, 2013). Cm: 400 μg/mL chloramphenicol (antibacterial control); ncAAs used for SPI are abbreviated above and depicted below the corresponding wells: cis/trans-4-fluoroproline ((4S/R-F)Pro), cis/trans-4-hydroxyproline ((4S/R-OH)Pro), cis/trans-methanoproline, proline (wild-type control). See Supplementary Information for assay details. Nisin structure including (methyl)lanthionine rings and NisP cleavage site (red triangle) depicted at the bottom, highlighting position of proline 9 (red circle) targeted for modification by ncAAs. (B) MS deconvolution chromatogram for recombinant nisin containing trans-4-hydroxyproline. Calculated masses (Da): [M+Na]+ – 8 H2O = 6779.21, [M+Na]+ – 7 H2O = 6795.21, [M+Na]+ – 6 H2O = 6813.21, [M+Na]+ – 5 H2O = 6831.21 (C) Compound spectrum for charged species of [M+Na]+ – 8 H2O.
