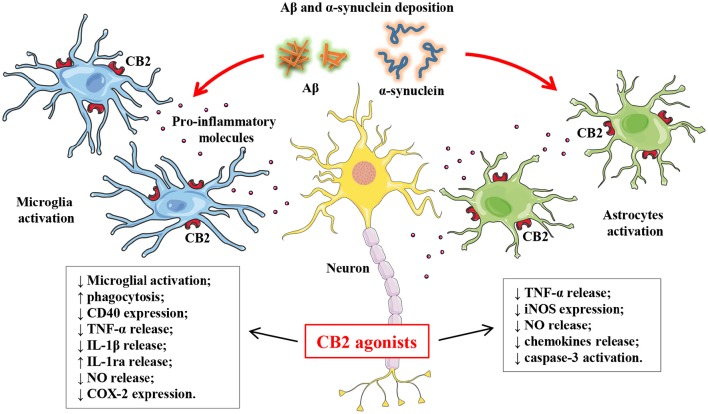
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions of CB2 agonists in AD and PD. AD and PD are characterized respectively by the deposition of Aβ and α-synuclein proteins which in turn are directly or indirectly involved in microglial and astrocytic activation. This activation of microglia and astrocytes triggers a neuroinflammatory and immune response which contributes to the progression of AD and PD. The pharmacological activation of microglial and astrocytic CB2 cannabinoid receptors with CB2 agonists is a promising therapeutic approach because it promotes anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects such as the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine release and an increases in anti-inflammatory molecules.