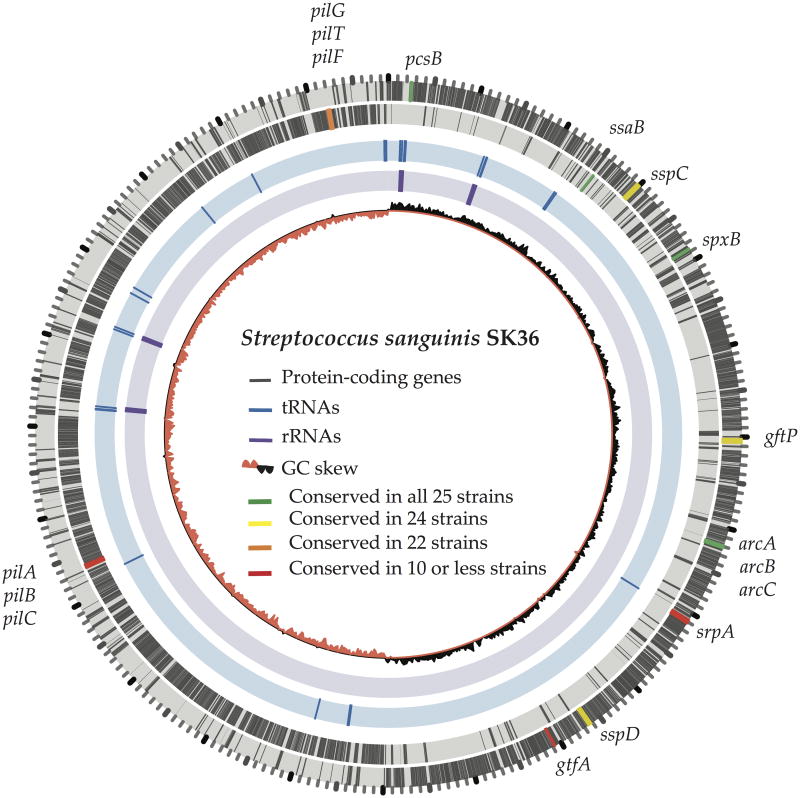
Fig. 2.
Genome of Streptococcus sanguinis SK36. The two outer rings illustrate protein-encoding genes (in grey) on forward and reverse strands, respectively. The position and conservation of several functional genes (Tab. 1) are also highlighted. The innermost ring shows the GC skew. Interestingly, most genes are located on the leading strand of each replichore. Additionally, most tRNAs (blue, ring 3) and rRNAs (purple, ring) are clustered around the origin of replication, possibly to optimize the growth rate.