Figure 2.
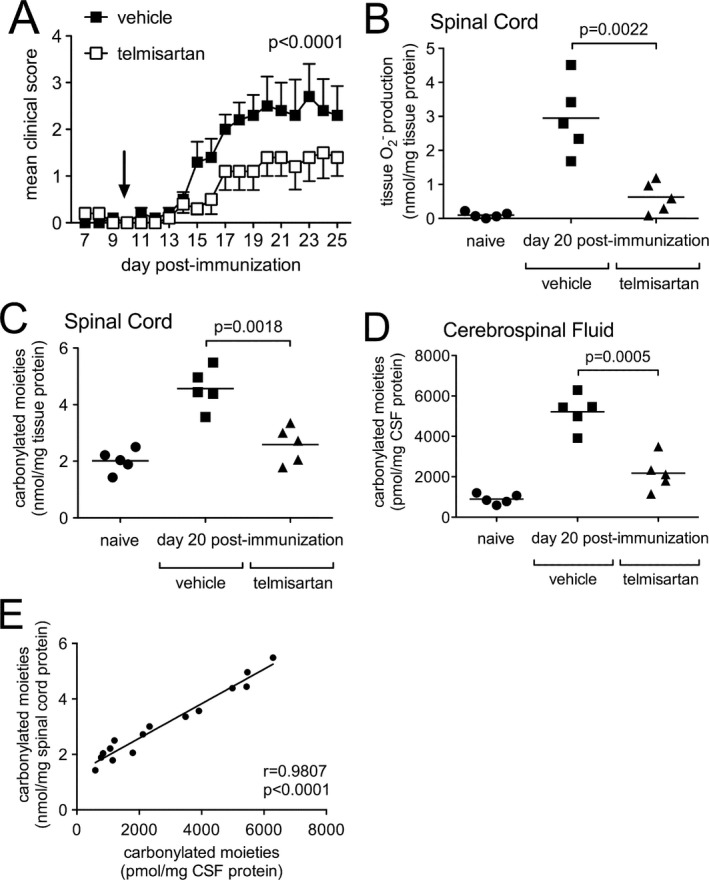
Systemic administration of telmisartan suppresses clinical disease severity, tissue ROS production, and protein carbonylation in the central nervous system of mice with EAE. (A) Mice with active immunization EAE were treated twice daily with telmisartan (n = 10) or a vehicle control (n = 10) beginning 10 days following disease induction (arrow). Clinical disease scores were significantly different between the two groups (P < 0.0001). (B) Telmisartan potently suppressed EAE‐induced tissue ROS production compared to mice given a vehicle control (P = 0.0022). (C, D) Telmisartan simultaneously inhibited the formation of carbonylated moieties directly in spinal cord tissue (P = 0.0018) and CSF (P = 0.0005) compared to a vehicle control. (E) Levels of carbonylated moieties in CSF and spinal cord were tightly correlated with each other in individual animals (P < 0.0001). CSF, cerebrospinal fluid.
