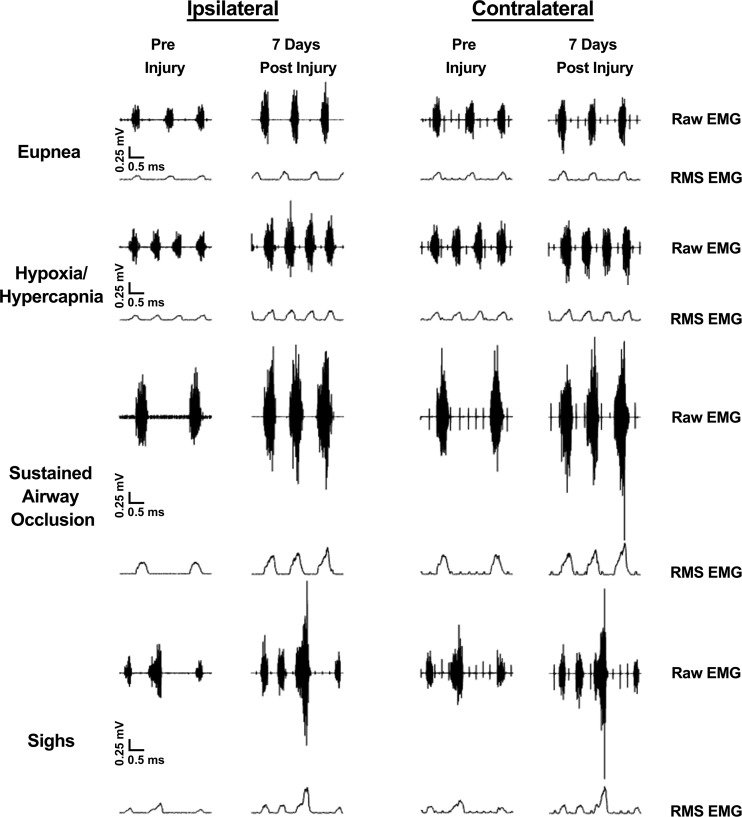
Fig. 4.
Representative ipsilateral and contralateral compound diaphragm EMG and root mean square (RMS) EMG recordings across eupnea, hypoxia-hypercapnia (10% O2, 5% CO2), airway occlusion, and spontaneous deep breath (sigh) from a C4 contusion animal at −1 and 7 days postinjury. Note increased diaphragm RMS EMG activity during sighs and airway occlusion compared with the preinjury levels.