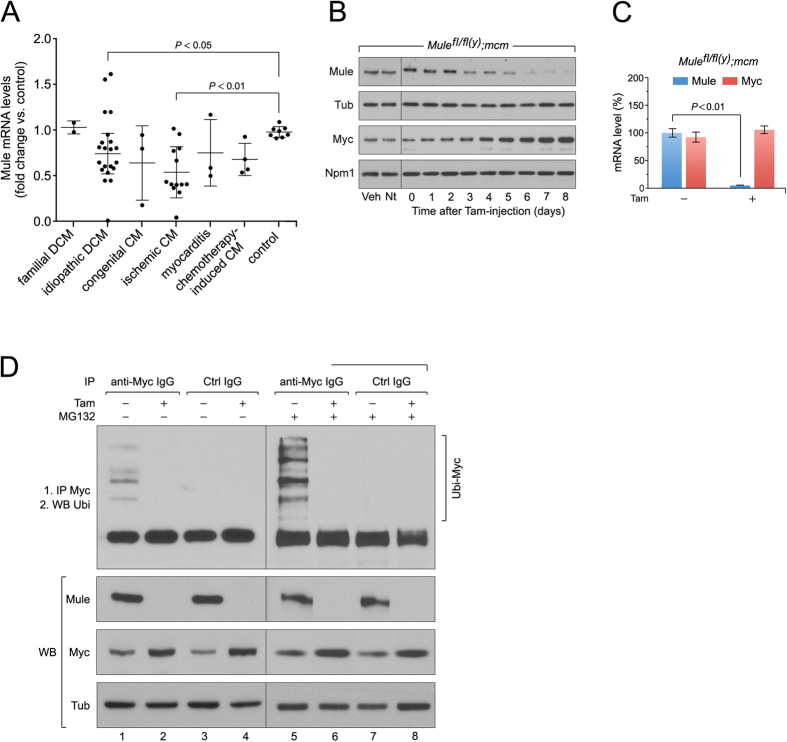
Figure 1. Acute genetic deletion of Mule induces concentric hypertrophy with cardiac dysfunction and premature death.
(A) Down-regulation of Mule mRNA levels in human end-stage heart failure determined by RT- qPCR. (B) To specifically inactivate Mule and Myc in the adult heart, we employed a tamoxifen (Tam) inducible Cre-loxP system in which Cre recombinase expression is controlled by the cardiomyocyte-specific myosin heavy chain 6 promoter (mcm). 4-hydroxytamoxifen (Tam) was injected intraperitoneally daily for four consecutive days in 10 week-old mice. The day of the last Tam injection was set as day zero. Veh, vehicle. Nt, no treatment. Immunoblot analysis of cytoplasmic Mule and nuclear Myc levels in left ventricular extracts (60 μg total protein/lane) of Mulefl/fl(y);mcm mice at 7 days post-Tam employing specific antibodies as indicated on the left. Animals were 12 weeks old at the time of analysis. For normalization, Western blots were probed with anti-tubulin (Tub) for cytoplasmic fractions, and anti-nucleophosmin (Npm1) for nuclear fractions. Immunoblots were repeated at least once with similar results. Transcript levels of Mule and Myc in Mulefl/fl(y);mcm mice at 7 d post-Tam as analyzed by RT-qPCR. n = 4. (C) Mule is indispensable for Myc protein stability in the heart by regulation of its ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation. At 7 d post-Tam. Mulefl/fl(y);mcm, mice were intraperitoneally injected with the proteasomal inhibitor MG132 or vehicle for 6 hours. LV lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Myc antibodies or normal rabbit IgG. Ubiquitinated Myc proteins in the immunoprecipitates were identified by immunoblotting with antibodies to ubiquitin. IgG, immunoglobulin G. IP, immunoprecipitation. Ubi, ubiquitin. WB, Western blot. One representative result of three independent experiments is depicted. Data are means ± s.e.m.