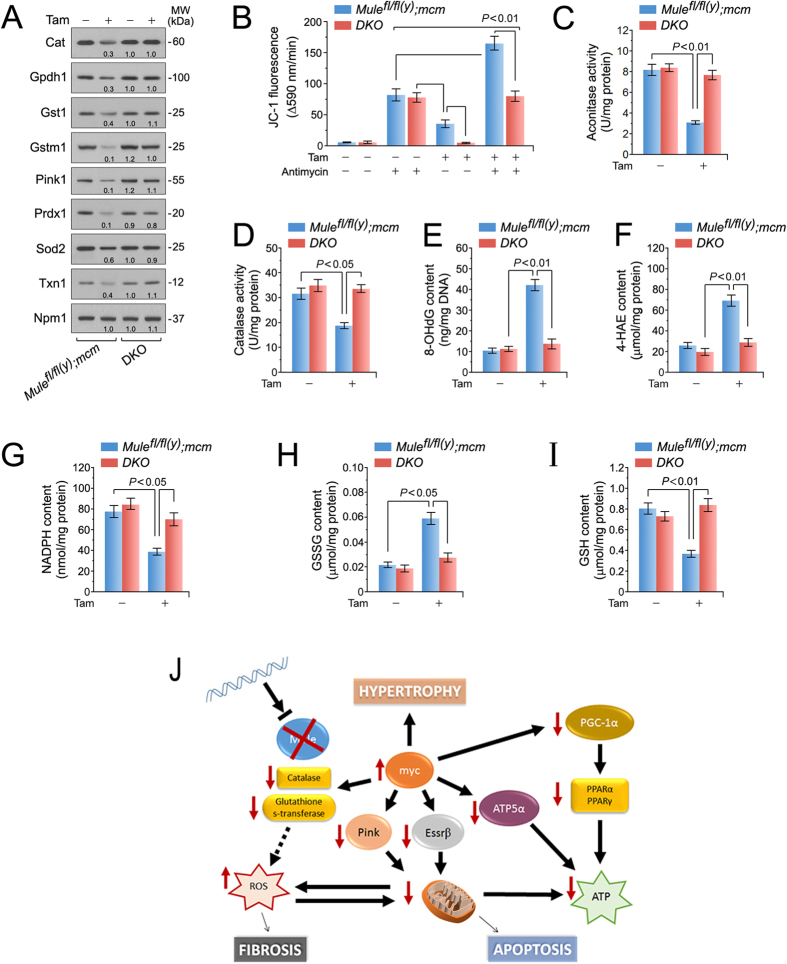
Figure 6. Enhanced oxidative stress in mice with cardiac-specific deletion of Mule.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of factors involved in detoxification processes of reactive oxygen species in left ventricular extracts of Mulefl/fl(y);mcm and DKO mice at 7 days post-Tam employing specific antibodies as indicated on the left. One representative result of three independent experiments is shown. (B) The membrane potential (ΔΨm) of mitochondria isolated from Mule mutant mice is susceptible to ROS-induced depolarization. Genetic co-ablation of Myc and Mule in DKO mice rescues antimycin induced decreases of ΔΨm in mitochondria derived from this double mutant strain. Isolated mitochondria, incubated with JC-1 (5 μg/mL), were treated with antimycin (50 μM). JC-1 emission at 535/595 nm was recorded at 1 reading/min for 30 min using a fluorescence spectrophotometer. The rate between two time points (Δemission at 595 nm/min) was calculated in the most linear range of decline for JC-1 fluorescence intensity. n = 4. (C,D) Mitochondrial aconitase (C) and catalase (D) activities were determined spectrophotometrically in ventricular samples from Mulefl/fl(y);mcm and DKO strains at 7 days post-Tam. n = 4. (E) Oxidative genomic DNA damage in the hearts of Mulefl/fl(y);mcm mice is abolished by genetic co-ablation of Myc in DKO animals. Concentrations of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8- OHdG), a biomarker for oxidative DNA damage in the indicated strains was determined by a competitive enzyme-linked ELISA employing 8-OHdG antibodies. n = 4. (F) Higher levels of 4-hydroxyalkenals (4-HAE), an indicator of ROS-dependent lipid peroxidation in ventricular extracts of Mulefl/fl(y);mcm compared with DKO. n = 4. (G) Significantly reduced levels of NADPH, an essential cofactor for the reduction of glutathione, in in ventricul*ar extracts of Mulefl/fl(y);mcm mice versus DKO. n = 4. (H,I) Decreased the reduced glutathione/oxidized glutathione (GSH/GSSG) ratios, an indicator of cardiac oxidative stress, in ventricular samples from Mulefl/fl(y);mcm mice that was prevented by Myc co-ablation in DKO. n = 4. Schematic model for Mule-mediated inhibition of Myc-dependent cardiac hypertrophy. In response to genetic ablation of Mule, Myc is activated and transcriptionally inhibits canonical downstream targets Pgc-1α and Pink1 promoting the development of heart failure by induction of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Data are means ± s.e.m.