Figure 3.
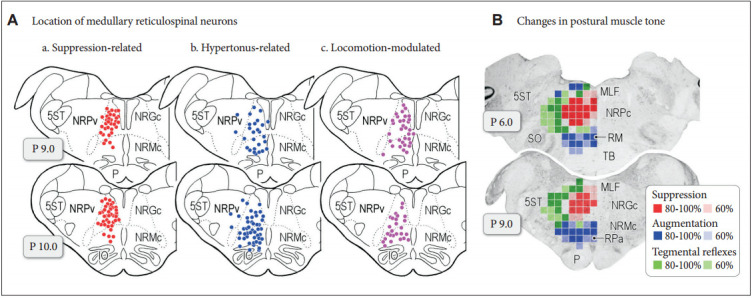
Functional organization of medullary reticulospinal systems in decerebrate cats. A: Locations of the medullary reticulospinal neurons relating to muscle tone suppression (a), muscle tone augmentation (hypertonus) (b), and locomotion (c). During reflex standing of the decerebrate cats, reticulospinal neurons with a firing frequency more than 10 Hz during reflex standing of decerebrate cats are judged as hypertonus-related reticulospinal neurons (b; n = 76). When carbachol (long-acting cholinomimetic agents) was injected into the pontine reticular formation muscle tone of decerebrate cats was abolished. Reticulospinal neurons of which firing frequency was increased to more than 10 Hz during carbachol-induced atonia are judged as atonia-related reticulospinal neurons (a; n = 75). During reflex standing (decerebrate rigidity) these cells usually had no spontaneous firing. Locomotion-related neurons (n = 59) were judged as those displaying rhythmic firing relating to step cycles of locomotion. Recording was made in both high decerebrated cats which displayed spontaneous locomotion and normal decerebrated cats with stimulation of the MLR. B: Results obtained from five animals are superimposed on representative coronal planes of the caudal pons and medulla. Sites from which either suppression (red), augmentation (blue), or tegmental reflexes (green) was elicited in more than three out of five animals are marked. Sites from which the stimulation induced postural changes in more than four animals are indicated by darker colored squares; conversely, light colored squares indicate that the postural changes were induced in three animals. Modified from Takakusaki et al. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2016;123:695-729, with permission of Springer [15]. P: pyramidal tract, MLF: medial longitudinal fasciculus, 5ST: spinal trigeminal tract, NRPc: nucleus reticularis pontis caudalis, TB: trapezoid body, RM: nucleus raphe magnus, SO: superior olive, NRGc: nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis, NRMc: nucleus reticularis magnocellularis, RPa: nucleus raphe pallidus, NRPv: nucleus reticulars parvocellularis.
