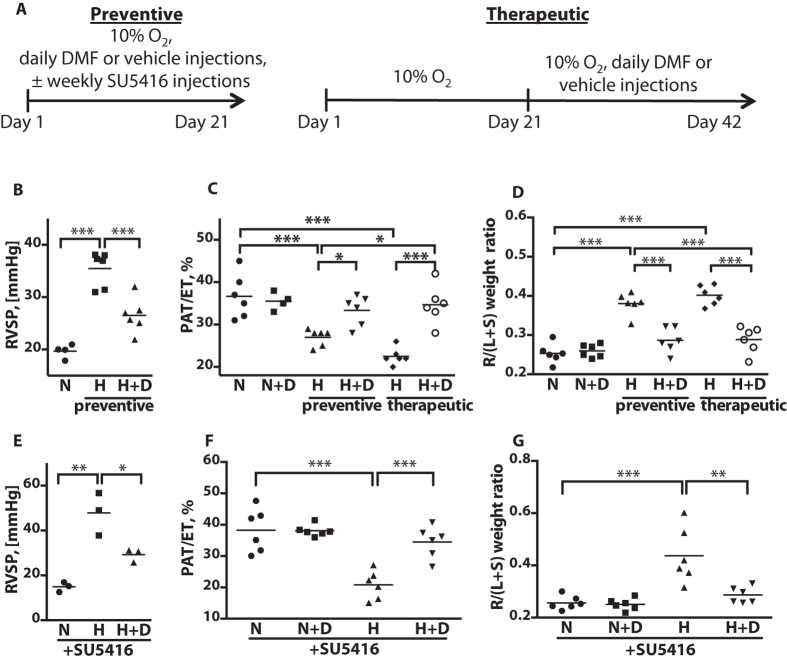
Figure 1. DMF abrogates hypoxia- and hypoxia/SU5416- induced increase in RV blood pressure and RV hypertrophy in vivo.
(A) Experimental design for preventive and therapeutic DMF treatment modes. In the preventive mode mice were kept in normoxia (N) or hypoxia (H) (10% O2) for 21 days and injected daily with 90 mg/kg DMF (D) or vehicle. In the therapeutic mode mice were kept in hypoxia for a total of 42 days with daily DMF injections starting at day 21. In the hypoxia/SU5416 model, mice were kept in hypoxia for 21 days and injected weekly with 20 mg/kg SU5416. (B,E) The RV systolic blood pressure (RVSP) was measured by catheterization for the mice in the preventive experiment and hypoxia/SU5416 mice. n = 6 mice per group. (C,F) Pulmonary acceleration time (PAT) and PAT as a fraction of ejection time (PAT/ET) were measured. n = 4–6 mice per group. (D,G) The weight ratios of the right ventricle to the left ventricle plus septum (S) (RV/(LV + S)) were calculated as indices of RV hypertrophy. n = 6 mice per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.